Melatonin rescues cell respiration impaired by hypoxia/reoxygenation in aortic endothelial cells and affects the mitochondrial bioenergetics targeting the F1FO-ATPase
- PMID: 40132239
- PMCID: PMC11985001
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103605
Melatonin rescues cell respiration impaired by hypoxia/reoxygenation in aortic endothelial cells and affects the mitochondrial bioenergetics targeting the F1FO-ATPase
Abstract
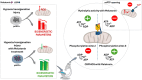
Melatonin is evaluated as a potential molecular therapy to counteract mitochondrial dysfunction caused by hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) in aortic endothelial cells (pAECs). The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening undergoes a desensitizing action coupled with a reduction of superoxide anion production in mitochondria treated with melatonin. The effect on mPTP has been attributed to the direct interaction of melatonin with the hydrophilic F1 domain of Ca2+-activated F1FO-ATPase. Mutual exclusion analysis highlights an overlapping binding site between melatonin and the specific F1 inhibitor NBD-Cl. The results are corroborated by melatonin inhibition of ATPase activity of the purified F1 domain in the presence of Ca2+, but not in the presence of natural cofactor Mg2+. Moreover, the impairment of bioenergetics parameters in pAECs metabolism and the increase of oxidative stress arising by H/R injury have been rescued in cells protected by melatonin treatment.
Keywords: F(1)F(O)-ATPase; H/R injury; Melatonin; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Mitochondrial permeability transition pore; ROS production.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Salvatore Nesci reports financial support was provided by European Union - Next Generation EU, M4C1, Progetto PRIN 2022 UNDER40 (MUR). If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
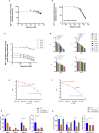
 ) and with 1 mM (
) and with 1 mM ( ) or 10 mM (
) or 10 mM ( ) melatonin. Data represent the mean ± SD (vertical bars) from at least three independent experiments carried out on different mitochondrial preparations. Statistical analysis was performed by Dunnett's test on each group vs the control (0 mM melatonin) (D). ∗ Indicate significantly different (∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001), ns indicate no significantly different.
) melatonin. Data represent the mean ± SD (vertical bars) from at least three independent experiments carried out on different mitochondrial preparations. Statistical analysis was performed by Dunnett's test on each group vs the control (0 mM melatonin) (D). ∗ Indicate significantly different (∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001), ns indicate no significantly different.


 ) and with (
) and with ( ) 1 mM melatonin and in H/R, without (
) 1 mM melatonin and in H/R, without ( ) and with (
) and with ( ) 1 mM Melatonin under basal respiration conditions and after addition of 1.5 μM oligomycin (olig), 1.0 μM FCCP and a mixture of 0.5 μM rotenone plus antimycin A (Rot + AA). Modulator injections are shown with arrows. D) Mitochondrial parameters (basal respiration, proton leak, maximal respiration, spare respiratory capacity and ATP production) in normoxia and H/R without (
) 1 mM Melatonin under basal respiration conditions and after addition of 1.5 μM oligomycin (olig), 1.0 μM FCCP and a mixture of 0.5 μM rotenone plus antimycin A (Rot + AA). Modulator injections are shown with arrows. D) Mitochondrial parameters (basal respiration, proton leak, maximal respiration, spare respiratory capacity and ATP production) in normoxia and H/R without ( ) or in the presence (
) or in the presence ( ) of 1 mM melatonin. E) Evaluation of superoxide anion production in pAECs in the Normoxia or H/R injury without (
) of 1 mM melatonin. E) Evaluation of superoxide anion production in pAECs in the Normoxia or H/R injury without ( ) or in the presence (
) or in the presence ( ) of 1 mM melatonin. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of four (D) and three (E) independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by Dunnett's test on each group vs the control (0 mM melatonin). ∗ Indicate significantly different (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01), ns indicate no significant difference.
) of 1 mM melatonin. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of four (D) and three (E) independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by Dunnett's test on each group vs the control (0 mM melatonin). ∗ Indicate significantly different (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01), ns indicate no significant difference.References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

