Low natalizumab trough concentrations are associated with reduced seroconversion of the John Cunningham virus in natalizumab-treated patients with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 40132877
- PMCID: PMC12573372
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp-2024-335761
Low natalizumab trough concentrations are associated with reduced seroconversion of the John Cunningham virus in natalizumab-treated patients with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Natalizumab is a highly effective drug for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS). A disadvantage of this treatment is the risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in patients who are seropositive for the John Cunningham virus (JCV). JCV seroconversion rates increase under natalizumab treatment compared with non-natalizumab using controls. The aim of this study was to assess whether lower natalizumab trough concentrations are associated with reduced JCV seroconversion compared with higher natalizumab trough concentrations.
Methods: Two overlapping cohorts of patients treated with intravenous natalizumab in the Netherlands were combined for this study. JCV seroconversion was assessed during periods of high (≥15 µg/mL) and low (<15 µg/mL) natalizumab trough concentrations. Low trough concentrations were mainly the result of trough concentration guided personalised extended interval dosing (EID). The seroconversion rates during high and low trough concentrations were compared using a generalised linear mixed model with a Poisson link function.
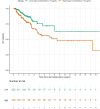
Results: A total of 357 patients from 21 hospitals in the Netherlands were included. The annual seroconversion rate of 8.4% observed in patients during periods of high trough concentrations (n=226) was 2.32 times higher than the seroconversion rate of 4.8% in patients during periods of low trough concentrations (n=252) (95% CI=1.32 to 4.08, p=0.0035).
Conclusions: The seroconversion rate observed in patients with MS with low trough concentrations was substantially lower compared with those with high trough concentrations during natalizumab treatment. This emphasises the importance of personalised EID, where intervals between infusions are prolonged to achieve lower natalizumab trough concentrations, to increase drug safety.
Keywords: MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: LMYG: nothing to disclose. AAT: received speakers fee from Biosynex. PMS: nothing to disclose. EH: has accepted (speaker and congress) fees from Merck Serono, Biogen Idec, Roche and Sanofi Genzyme. EMPEZ: reports advisory boards/consultancy fees for Merck, Novartis, Genzyme and Roche. LCvR: nothing to disclose. CEPvM: nothing to disclose. AV: nothing to disclose. PM: nothing to disclose. BW: nothing to disclose. NFK: nothing to disclose. ELJH: nothing to disclose. JvE: reports honoraria for advisory boards and/or speakers fee from Merck Serono, Biogen Idec, Sanofi Genzyme, Roche and Novartis. CMR: nothing to disclose. JJK: nothing to disclose. ME: nothing to disclose. JvG: nothing to disclose. JN: nothing to disclose. LGFS: nothing to disclose. MEK: nothing to disclose. EPJA: nothing to disclose. WHB: nothing to disclose. EMS: nothing to disclose. BVO: nothing to disclose. BADJ: nothing to disclose. BMJU: reports research support and/or consultancy fees from Genzyme, Biogen Idec, Novartis, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Merck Serono, Roche, and Immunic Therapeutics. BIL-W: nothing to disclose. FCL: nothing to disclose. TR: received funding for research from Genmab and consultancy fees from Novartis. JK: has received research grants for multicentre investigator initiated trials DOT-MS trial, ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04260711 (ZonMW) and BLOOMS trial (ZonMW and Treatmeds), ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05296161); received consulting fees for F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Biogen, Teva, Merck, Novartis and Sanofi/Genzyme (all payments to institution); reports speaker relationships with F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Biogen, Immunic, Teva, Merck, Novartis and Sanofi/Genzyme (all payments to institution); adjudication committee of MS clinical trials of Immunic (payments to institution only). ZLEvK: nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
