Enzymatic cleavage of model lignin dimers depends on pH, enzyme, and bond type
- PMID: 40133407
- PMCID: PMC11937299
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-88571-7
Enzymatic cleavage of model lignin dimers depends on pH, enzyme, and bond type
Abstract
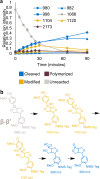
Lignin is composed of phenylpropanoid monomers linked by ether and carbon-carbon bonds to form a complex heterogeneous structure. Bond-specific studies of lignin-modifying enzymes (LMEs; e.g., laccases and peroxidases) are limited by the polymerization of model lignin substrates and repolymerization of cleavage products. Here we present a high throughput platform to screen LME activities on four tagged model lignin compounds that represent the β-O-4', β-β', 5-5', and 4-O-5' linkages in lignin. We utilized nanostructure-initiator mass spectrometry (NIMS) and model lignin compounds with tags containing perfluorinated and cationic moieties, which effectively limit polymerization and condensation of the substrates and their degrading products. Sub-microliter sample droplets were printed on the NIMS chip with a novel robotics method. This rapid platform enabled characterization of LMEs across a range of pH 3-10 and relative quantification of modified (typically oxidized), cleaved, and polymerized products. All tested enzymes oxidized the four substrates and cleaved the β-O-4' and β-β' substrates to monomeric products. We discovered that the active pH range depended on both the substrate and the enzyme type. This has important applications for biomass conversion to biofuels and bioproducts, where the relative percentages of different bond types in lignin varies depending on feedstock and chemical pretreatment methods.
Keywords: Laccase; Lignin; Mass spectrometry; Peroxidase.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zakzeski, J., Bruijnincx, P. C. A., Jongerius, A. L. & Weckhuysen, B. M. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem. Rev.110, 3552–3599 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Luo, H. & Abu-Omar, M. M. Chemicals From Lignin. In Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies. 573–585 (Elsevier, 2017). 10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.10235-0
-
- Shrestha, S. et al. Perspective on lignin conversion strategies that enable next generation biorefineries. ChemSusChem, 202301460–202301461 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Roy, R., Rahman, M. S., Amit, T. A. & Jadhav, B. Recent advances in lignin depolymerization techniques: a comparative overview of traditional and greener approaches. Biomass (Switzerland). 2, 130–154 (2022).
-
- Curran, L. M. C. L. K., Thanh, L., Pham, M., Sale, K. L. & Simmons, B. A. Review of advances in the development of laccases for the valorization of lignin to enable the production of lignocellulosic biofuels and bioproducts. Biotechnol. Adv.10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107809 (2021). - PubMed

