Persistent epigenetic memory of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in monocyte-derived macrophages
- PMID: 40133533
- PMCID: PMC11965535
- DOI: 10.1038/s44320-025-00093-6
Persistent epigenetic memory of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in monocyte-derived macrophages
Abstract
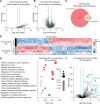
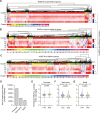
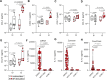
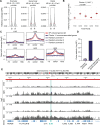
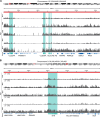
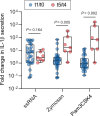
Immune memory plays a critical role in the development of durable antimicrobial immune responses. How precisely mRNA vaccines train innate immune cells to shape protective host defense mechanisms remains unknown. Here we show that SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination significantly establishes histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) at promoters of human monocyte-derived macrophages, suggesting epigenetic memory. However, we found that two consecutive vaccinations were required for the persistence of H3K27ac, which matched with pro-inflammatory innate immune-associated transcriptional changes and antigen-mediated cytokine secretion. H3K27ac at promoter regions were preserved for six months and a single mRNA booster vaccine potently restored their levels and release of macrophage-derived cytokines. Interestingly, we found that H3K27ac at promoters is enriched for G-quadruplex DNA secondary structure-forming sequences in macrophage-derived nucleosome-depleted regions, linking epigenetic memory to nucleic acid structure. Collectively, these findings reveal that mRNA vaccines induce a highly dynamic and persistent training of innate immune cells enabling a sustained pro-inflammatory immune response.
Keywords: Epigenetic Memory; G-quadruplex; H3K27ac; SARS-Cov-2 mRNA Vaccination; Trained Innate Immunity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Esnault C, Magat T, Zine El Aabidine A, Garcia-Oliver E, Cucchiarini A, Bouchouika S, Lleres D, Goerke L, Luo Y, Verga D et al (2023) G4access identifies G-quadruplexes and their associations with open chromatin and imprinting control regions. Nat Genet 55:1359–1369 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 01KI2108/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
- IdEpiCo/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
- NaFoUniMedCovid19 grant COVIM 01KX2021/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
- FI 773/15-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- SFB1403/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- INST 216/1057-2/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- HA 8562/4-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- HA 8562/5-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- INST 216/1317-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- TTU-TB grant 02.913/Deutsches Zentrum für Infektionsforschung (DZIF)
- TTU-TB grant 02.814/Deutsches Zentrum für Infektionsforschung (DZIF)
- ERA4TB/European Union Horizon 2020 program
- 01KX2121/Federal Ministry of Education and Research
- EXC 2030-390661388/German Excellence Strategy
- 10.22.1.010MN/Fritz Thyssen Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

