Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Coronary Artery Calcium-Scoring CT for Pulmonary Nodule Detection: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 40134084
- PMCID: PMC11955396
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2024.0050
Deep Learning-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Coronary Artery Calcium-Scoring CT for Pulmonary Nodule Detection: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the feasibility and utility of deep learning-based computer-aided diagnosis (DL-CAD) for the detection of pulmonary nodules on coronary artery calcium (CAC)-scoring computed tomography (CT).
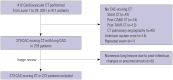
Materials and methods: This retrospective study included 273 patients (aged 63.9±13.2 years; 129 men) who underwent CAC-scoring CT. A DL-CAD system based on thin-section images was used for pulmonary nodule detection, and two independent junior readers reviewed the standard CAC-scoring CT scans with and without referencing DL-CAD results. A reference standard was established through the consensus of two experienced radiologists. Sensitivity, positive predictive value, and F1-score were assessed on a per-nodule and per-patient basis. The patients' medical records were monitored until November 2023.
Results: A total of 269 nodules were identified in 129 patients. With DL-CAD assistance, the readers' sensitivity significantly improved (65% vs. 80% for reader 1; 82% vs. 86% for reader 2; all p<0.001), without a notable increase in the number of false-positives per case (0.11 vs. 0.13, p=0.078 for reader 1; 0.11 vs. 0.11, p>0.999 for reader 2). Per-patient analysis also enhanced sensitivity with DL-CAD assistance (73% vs. 84%, p<0.001 for reader 1; 89% vs. 91%, p=0.250 for reader 2). During follow-up, lung cancer was diagnosed in four patients (1.5%). Among them, two had lesions detected on CAC-scoring CT, both of which were successfully identified by DL-CAD.
Conclusion: DL-CAD based on thin-section images can assist less experienced readers in detecting pulmonary nodules on CAC-scoring CT scans, improving detection sensitivity without significantly increasing false-positives.
Keywords: Computer-aided diagnosis; X-ray computed; deep learning; diagnostic performance; lung; tomography.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Gupta A, Bera K, Kikano E, Pierce JD, Gan J, Rajdev M, et al. Coronary artery calcium scoring: current status and future directions. Radiographics. 2022;42:947–967. - PubMed
-
- Hecht HS, Henschke C, Yankelevitz D, Fuster V, Narula J. Combined detection of coronary artery disease and lung cancer. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2792–2796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

