Sirolimus treatment for intractable vascular anomalies (SIVA): An open-label, single-arm, multicenter, prospective trial
- PMID: 40134353
- PMCID: PMC11937875
- DOI: 10.1111/ped.70002
Sirolimus treatment for intractable vascular anomalies (SIVA): An open-label, single-arm, multicenter, prospective trial
Abstract
Background: Intractable vascular anomalies (VAs), including vascular tumors and venous, lymphatic, and mixed malformations, often have severe symptoms and a poor prognosis, highlighting the need for new treatments. We conducted a prospective trial of sirolimus (tablet and granule forms) for the treatment of VAs.
Methods: In this open-label, single-arm, multicenter trial across four Japanese institutions, patients with VAs received oral sirolimus daily, targeting a trough concentration of 5-15 ng/mL. We evaluated response rates (radiological volume changes in lesions), skin lesions, performance status, respiratory function, visceral symptoms (bleeding, pain), laboratory data, quality of life, and safety at 12, 24, and 52 weeks.
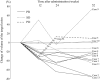
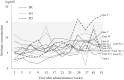
Results: Thirteen patients with VAs were treated with sirolimus. Seven patients (53.8%; 95% confidence interval: 25.1%-80.8%) showed a partial radiological response at 24 weeks, with no complete responses, and 61.5% had a partial response by 12 weeks, with little subsequent change in patients who had stable disease thereafter. Improvements in skin lesions, blood coagulation, and activities of daily living were noted. Common adverse events included stomatitis, dermatitis, diarrhea, and fever.
Conclusions: Sirolimus may reduce VA tissue volume and potentially improve symptoms and activities of daily living in patients with VAs.
Keywords: mammalian target of rapamycin; sirolimus granule; vascular malformations; vascular tumors; venous malformations.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pediatrics International published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Pediatric Society.
Figures

References
-
- Freixo C, Ferreira V, Martins J, Almeida R, Caldeira D, Rosa M, et al. Efficacy and safety of sirolimus in the treatment of vascular anomalies: a systematic review. J Vasc Surg. 2020;71:318–327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

