Foveal vision reduces neural resources in agent-based game learning
- PMID: 40134416
- PMCID: PMC11933080
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1547264
Foveal vision reduces neural resources in agent-based game learning
Abstract
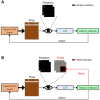
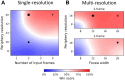
Efficient processing of information is crucial for the optimization of neural resources in both biological and artificial visual systems. In this paper, we study the efficiency that may be obtained via the use of a fovea. Using biologically-motivated agents, we study visual information processing, learning, and decision making in a controlled artificial environment, namely the Atari Pong video game. We compare the resources necessary to play Pong between agents with and without a fovea. Our study shows that a fovea can significantly reduce the neural resources, in the form of number of neurons, number of synapses, and number of computations, while at the same time maintaining performance at playing Pong. To our knowledge, this is the first study in which an agent must simultaneously optimize its visual system, along with its decision making and action generation capabilities. That is, the visual system is integral to a complete agent.
Keywords: multi-resolution sensory integration; neural resources; neuromorphic computing; reinforcement learning; visual neuroscience.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Kunde, Tao and Sornborger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Single neuromorphic memristor closely emulates multiple synaptic mechanisms for energy efficient neural networks.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 13;15(1):6898. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51093-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39138160 Free PMC article.
-
Playing Atari with few neurons: Improving the efficacy of reinforcement learning by decoupling feature extraction and decision making.Auton Agent Multi Agent Syst. 2021;35(2):17. doi: 10.1007/s10458-021-09497-8. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Auton Agent Multi Agent Syst. 2021. PMID: 34720684 Free PMC article.
-
Demonstrating Advantages of Neuromorphic Computation: A Pilot Study.Front Neurosci. 2019 Mar 26;13:260. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00260. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30971881 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromorphic Engineering: From Biological to Spike-Based Hardware Nervous Systems.Adv Mater. 2020 Dec;32(52):e2003610. doi: 10.1002/adma.202003610. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 33165986 Review.
-
Perceptual learning during action video game playing.Top Cogn Sci. 2010 Apr;2(2):202-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-8765.2009.01054.x. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Top Cogn Sci. 2010. PMID: 25163784 Review.
References
-
- Adhikari A., Ren Y. (2021). RL-PONG: Playing Pong From Pixels. Project Proposal, CSCE 790-001: Deep Reinforcement Learning and Search.
-
- Baker B., Akkaya I., Zhokov P., Huizinga J., Tang J., Ecoffet A., et al. . (2022). Video pretraining (VPT): learning to act by watching unlabeled online videos. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 24639–24654. 10.48550/arXiv.2206.11795 - DOI
-
- Chavez Arana D., Renner A., Sornborger A. (2023). “Spiking LCA in a neural circuit with dictionary learning and synaptic normalization,” in Proceedings of the 2023 Annual Neuro-Inspired Computational Elements Conference (New York, NY: ACM; ), 47–51. 10.1145/3584954.3584968 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

