Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Periodontology: A Review
- PMID: 40134460
- PMCID: PMC11935294
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81162
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Periodontology: A Review
Abstract
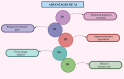
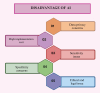
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing each of the healthcare fields, including periodontology, through the improvement of every diagnosis, treatment plan, and the handling of all patients. AI-driven technologies such as machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision are incorporated into radiographic analysis, automated disease detection, and prognosis prediction. These improvements effectively enable the early detection of periodontal diseases and efficient classification of disease severity. In addition, they allow for specially personalized treatment approaches. AI makes automated periodontal charting, virtual patient monitoring, and decision support systems easier, which improve clinical outcomes and patient care. Despite its immense potential, many substantial difficulties remain, such as data privacy, algorithm reliability, and the meaningful need for clinical validation. This review indicates the revolutionary function of AI in many current dental works and explores all present uses, advantages, limits, and possibilities in periodontology.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; computer program; endodontics; exert influence; gum infection and disease; knowledge engineering; operating system; periodontology; tooth-related disease.
Copyright © 2025, Patel et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Evaluation of salivary parameters and oral health status in periodontally healthy subjects and chronic periodontitis subjects. Kurien VTV, Shanker RK, Hegde S, Onisha V, Pillai SAS. Adv Hum Biol. 2024;14:203–209.
-
- Evaluation of periodontal status amongst the diabetic patients visiting private dental clinic in ahmedabad using CPITN. Patel E, Parikh H, Shah R, Mandaliya D, Vishwkarama S, Nayak S. Adv Hum Biol. 2022;12:249.
-
- Validation of a dental image-analyzer tool to measure the radiographic defect angle of the intrabony defect in periodontitis patients. Moutinho RP, Coelho L, Silva A, Lobo Pereira JA, Pinto M, Baptista IP. J Periodontal Res. 2012;47:695–700. - PubMed
-
- Awareness of physicians about the relationship of periodontal diseases and systemic conditions in Nashik district: a questionnaire study [Online Ahead of Print] Patil SS, Kulkarni KN, Patil C, Ojha M, Lihe V, Waghmare S. Adv Hum Biol. 2025
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
