Impact of Antibiotic Duration on Gut Microbiome Composition and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Substudy of the BALANCE Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40134637
- PMCID: PMC11935739
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf137
Impact of Antibiotic Duration on Gut Microbiome Composition and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Substudy of the BALANCE Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Maintaining a diverse gut microbiome and minimizing antimicrobial resistance gene (ARG) carriage through reduced antibiotic utilization may decrease antimicrobial resistance. We compared gut microbiome disruption and ARG carriage following 7 or 14 days of antibiotics for treatment of bacteremia in a substudy of the BALANCE randomized controlled trial.
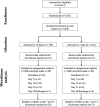
Methods: The BALANCE randomized controlled trial enrolled 3631 participants with bacteremia, who were randomized 1:1 to receive 7 or 14 days of antibiotics. Rectal swabs were collected from 131 participants and analyzed with metagenomic sequencing to characterize the gut microbiome and ARGs. The primary outcome was change in gut microbiome diversity at day 7 vs 14.
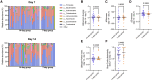
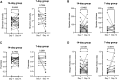
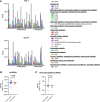
Results: Forty-one participants (n = 28 in the 14-day group, n = 13 in the 7-day group) had samples available for the primary analysis, with an imbalance in piperacillin-tazobactam exposure between groups. Change in gut microbiome diversity at day 7 vs 14 was comparable between the 14-day group (median, 0.07; IQR, -0.46 to +0.51) and 7-day group (median, 0.19; IQR, -0.77 to +0.22; P = .49). Change in ARG abundance at day 7 vs 14 did not differ by treatment duration, nor did the abundance of individual ARGs. We did not observe any change in gut microbiome diversity or ARG carriage at enrollment vs day 7.
Conclusions: In this subset of patients from the BALANCE randomized controlled trial, we did not detect greater gut microbiome disruption or ARG carriage among participants who received 14 vs 7 days of antibiotics, but we were limited by small sample size and imbalances between groups.
Keywords: antibiotics; antimicrobial resistance; antimicrobial stewardship; bacteremia; microbiome.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Antimicrobial resistance: global report on surveillance. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2014. Available at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/112642. Accessed 4 September 2024.
-
- Dellit TH, Owens RC, McGowan JE, et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America guidelines for developing an institutional program to enhance antimicrobial stewardship. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44:159–77. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

