Phase 1 trial of hypofractionated stereotactic re-irradiation in combination with nivolumab, ipilimumab, and bevacizumab for recurrent high-grade gliomas
- PMID: 40134851
- PMCID: PMC11934552
- DOI: 10.1093/noajnl/vdaf033
Phase 1 trial of hypofractionated stereotactic re-irradiation in combination with nivolumab, ipilimumab, and bevacizumab for recurrent high-grade gliomas
Abstract
Background: Our previous clinical investigation suggested that hypofractionated stereotactic re-irradiation (HFSRT) and PD-1 blockade may act synergistically to enhance the immune response against glioma. This subsequent trial investigated the dual blockade of CTLA4 and PD-1 in combination with HFSRT and bevacizumab.
Methods: This phase I study enrolled eligible patients with bevacizumab-naïve recurrent glioblastoma or anaplastic astrocytoma. Participants received nivolumab, ipilimumab, and bevacizumab concurrently with HFSRT (3000 cGy in 5 fractions). Subsequently, nivolumab, ipilimumab, and bevacizumab were administered for a total of 4 cycles followed by nivolumab and bevacizumab until progression. The primary end point of this study was the safety and tolerability of HFSRT in combination with nivolumab, ipilimumab, and bevacizumab in patients with recurrent HGGs. Secondary end points included 6-month survival and 9-month survival.
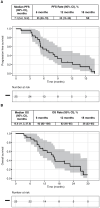
Results: Twenty-six patients were treated. Treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) of grade 3 or 4 were observed in 12 (48%) evaluable patients with no unexpected TRAEs. Six months and 9 months survival were 92% (95% CI, 82-100%) and 75% (95% CI, 60-95%), respectively. The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 7.1 months (95% CI, 5.2-12.2) and 15.6 months (95% CI, 11.3-27.0), respectively.
Conclusions: The combination of HFSRT with ipilimumab, nivolumab, and bevacizumab is safe. Our results underscore the potential synergies between stereotactic re-irradiation and checkpoint immunotherapy in patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas.
Keywords: glioblastoma; high-grade glioma; ipilimumab; nivolumab; stereotactic re-irradiation.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press, the Society for Neuro-Oncology and the European Association of Neuro-Oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Reardon DA, Gokhale PC, Klein SR, et al.Glioblastoma eradication following immune checkpoint blockade in an Orthotopic, Immunocompetent Model. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4(2):124–135. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources