Bladder cancer biomarkers
- PMID: 40135048
- PMCID: PMC11933887
- DOI: 10.37349/etat.2025.1002301
Bladder cancer biomarkers
Abstract
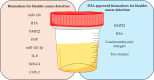
Bladder cancer (BCa) is among the most frequently diagnosed urinary tract cancers, characterized by a high recurrence rate and significant clinical heterogeneity. Effective diagnosis and treatment of BCa demand continuous advancements in medical technologies, particularly given the limitations of classical methods such as cystoscopy and urine cytology. A comprehensive search of PubMed and Web of Science was conducted using relevant keywords to structure this narrative review. Additionally, specialist journals were reviewed. Only articles in English were included, with selection based on titles, abstracts, and availability of full texts. In recent years, biomarkers have emerged as crucial tools complementing traditional techniques, providing more precise, sensitive, and non-invasive methods for early detection, prognosis, and monitoring treatment response in BCa. Molecular, genetic, and protein biomarkers enable a deeper understanding of BCa biology, creating opportunities for personalized therapy tailored to individual patient needs. However, despite their potential, certain challenges remain, including standardization, validation, and integration into routine clinical practice. This review highlights recent advancements in BCa biomarkers and their transformative potential in oncological care. It underscores the importance of incorporating these innovations to refine diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Modern diagnostic and prognostic tools for BCa can enhance treatment outcomes by enabling early disease detection and reducing recurrence risks. This progress promises to improve patients' quality of life by minimizing disease burden and fostering effective, tailored care strategies.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; biomarkers; diagnostic; monitoring; predictive biomarkers; prognostic; urothelial cancer.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Leslie SW, Soon-Sutton TL, Aeddula NR. Bladder Cancer. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
