Vesicle inhibition reduces Candida biofilm resistance
- PMID: 40135881
- PMCID: PMC12057333
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00045-25
Vesicle inhibition reduces Candida biofilm resistance
Abstract
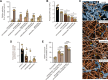
Candida biofilm matrix components are delivered to the extracellular space by vesicles where they deposit and confer biofilm-associated drug resistance. Here, we present evidence that drugs designed to inhibit mammalian exosome production exhibit similar effects on C. albicans extracellular vesicles, ultimately eliminating biofilm matrix assembly. We find that vesicle reduction renders biofilm communities susceptible to the antifungal fluconazole. Our findings argue that vesicle trafficking pathways represent a promising target to optimize for recalcitrant fungal biofilms.
Keywords: Candida albicans; antifungal resistance; biofilms; extracellular matrix; vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andes DR, Safdar N, Baddley JW, Playford G, Reboli AC, Rex JH, Sobel JD, Pappas PG, Kullberg BJ, Mycoses Study Group . 2012. Impact of treatment strategy on outcomes in patients with candidemia and other forms of invasive candidiasis: a patient-level quantitative review of randomized trials. Clin Infect Dis 54:1110–1122. doi:10.1093/cid/cis021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zarnowski R, Westler WM, Lacmbouh GA, Marita JM, Bothe JR, Bernhardt J, Lounes-Hadj Sahraoui A, Fontaine J, Sanchez H, Hatfield RD, Ntambi JM, Nett JE, Mitchell AP, Andes DR. 2014. Novel entries in a fungal biofilm matrix encyclopedia. mBio 5:e01333-14. doi:10.1128/mBio.01333-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

