Early 2022 breakthrough infection sera from India target the conserved cryptic class 5 epitope to counteract immune escape by SARS-CoV-2 variants
- PMID: 40135898
- PMCID: PMC11998512
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00051-25
Early 2022 breakthrough infection sera from India target the conserved cryptic class 5 epitope to counteract immune escape by SARS-CoV-2 variants
Abstract
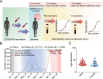
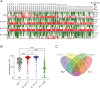
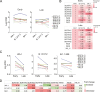
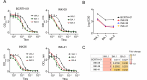
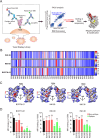
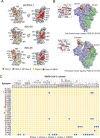
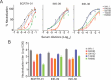
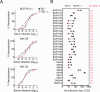
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the vast majority of epitope mapping studies have focused on sera from mRNA-vaccinated populations from high-income countries. In contrast, here, we report an analysis of 164 serum samples isolated from patients with breakthrough infection in India during early 2022 who received two doses of the ChAdOx viral vector vaccine. Sera were screened for neutralization breadth against wild-type (WT), Kappa, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 viruses. Three sera with the highest neutralization breadth and potency were selected for epitope mapping, using charged scanning mutagenesis coupled with yeast surface display and next-generation sequencing. The mapped sera primarily targeted the recently identified class 5 cryptic epitope and, to a lesser extent, the class 1 and class 4 epitopes. The class 5 epitope is completely conserved across all severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants and for most sarbecoviruses. Based on these observations, an additional 26 sera were characterized, and all showed a broad neutralizing activity, including against XBB.1.5. This is in contrast with the results obtained with the sera from individuals receiving multiple doses of original and updated mRNA vaccines, where impaired neutralization of XBB and later variants of concern (VOCs) were observed. Our study demonstrates that two doses of the ChAdOx vaccine in a highly exposed population were sufficient to drive substantial neutralization breadth against emerging and upcoming variants of concern. These data highlight the important role of hybrid immunity in conferring broad protection and inform future vaccine strategies to protect against rapidly mutating viruses.
Importance: Worldwide implementation of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines and the parallel emergence of newer severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants have shaped the humoral immune response in a population-specific manner. While characterizing this immune response is important for monitoring disease progression at the population level, it is also imperative for developing effective countermeasures in the form of novel vaccines and therapeutics. India has implemented the world's second largest COVID-19 vaccination drive and encountered a large number of post-vaccination "breakthrough" infections. From a cohort of patients with breakthrough infection, we identified individuals whose sera showed broadly neutralizing immunity against different SARS-CoV-2 variants. Interestingly, these sera primarily target a novel cryptic epitope, which was not identified in previous population-level studies conducted in Western countries. This rare cryptic epitope remains conserved across all SARS-CoV-2 variants, including recently emerged ones and for the SARS-like coronaviruses that may cause future outbreaks, thus representing a potential target for future vaccines.
Keywords: Omicron subvariant XBB.1.5; SARS-CoV-2; breakthrough infection; class 5/RBD8 epitopes; convalescent serum; epitope mapping; immune escape; neutralizing antibodies; spike protein RBD; yeast display library.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ecdc.europa . 2025. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern as of 28 February 2025. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern
-
- Our World in Data . 2024. Coronavirus (COVID-19) vaccinations. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
-
- Doshi RH, Nsasiirwe S, Dahlke M, Atagbaza A, Aluta OE, Tatsinkou AB, Dauda E, Vilajeliu A, Gurung S, Tusiime J, Braka F, Bwaka A, Wanyoike S, Brooks DJ, Blanc DC, Alexander JPJ, Dahl BA, Lindstrand A, Wiysonge CS. 2024. COVID-19 vaccination coverage - world health organization African region, 2021-2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 73:307–311. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7314a3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ministry of health and family welfare G of I. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. 2025. Govt of India: COVID-19 data. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

