Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions
- PMID: 40136378
- PMCID: PMC11941682
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol32030174
Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in Taiwan. It is often associated with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene, with common mutations accounting for approximately 85% of all EGFR-related cases. However, the remaining 15% are caused by uncommon mutations in EGFR, mainly insertions in exon 20 (about 4%). The response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) can vary markedly with exon 20 insertions. However, few prior large-scale studies have examined patients with these EGFR mutations.
Methods: This study combines the databases of several large hospitals in Taiwan to analyze the effects and clinical significance of rare EGFR mutations on responses to EGFR-TKIs, considering the changes in medication.
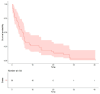
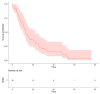
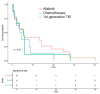
Results: This study enrolled 38 patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR exon 20 insertions. It assessed the correlations of various predictors with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). It showed that among those with EGFR exon 20 insertions, the median PFS was 5.15 months, and OS reached 13 months. The median PFS was 5.4 months for afatinib, 5.7 months for chemotherapy, and 4.3 months for first-generation EGFR-TKIs.
Conclusions: EGFR-TKIs may be considered as an alternative treatment option for patients with EGFR exon 20 insertions in cases where the currently recommended therapies, such as chemotherapy with or without amivantamab, are either unavailable or intolerable. The potential use of afatinib for specific patients in this context depends on the precise characteristics of their mutation and remains to be determined.
Keywords: exon 20 insertions; non-small-cell lung cancer; rare EGFR Mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Naidoo J., Sima C.S., Rodriguez K., Busby N., Nafa K., Ladanyi M., Riely G.J., Kris M.G., Arcila M.E., Yu H.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions in advanced lung adenocarcinomas: Clinical outcomes and response to erlotinib. Cancer. 2015;121:3212–3220. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29493. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arcila M.E., Nafa K., Chaft J.E., Rekhtman N., Lau C., Reva B.A., Zakowski M.F., Kris M.G., Ladanyi M. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013;12:220–229. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yasuda H., Park E., Yun C.-H., Sng N.J., Lucena-Araujo A.R., Yeo W.-L., Huberman M.S., Cohen D.W., Nakayama S., Ishioka K., et al. Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5:216ra177. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007205. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu J.-Y., Yu C.-J., Chang Y.-C., Yang C.-H., Shih J.-Y., Yang P.-C. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:3812–3821. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3408. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

