Research Progress on the Relationship Between PRPF8 and Cancer
- PMID: 40136404
- PMCID: PMC11941625
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47030150
Research Progress on the Relationship Between PRPF8 and Cancer
Abstract
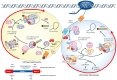
Alternative splicing (AS) plays a crucial role in regulating gene expression and protein diversity, influencing both normal cellular function and pathological conditions, including cancer. Protein pre-mRNA processing factor 8 (PRPF8), a core component of the spliceosome, is integral to the splicing process, ensuring accurate gene transcription and spliceosome assembly. Disruptions in PRPF8 function are linked to a variety of cancers, as mutations in this gene can induce abnormal splicing events that contribute to tumorigenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance. This review provides an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms by which PRPF8 regulates tumorigenesis through AS, exploring its role in diverse cancer types, including breast, liver, myeloid, and colorectal cancers. Furthermore, we examine the molecular pathways associated with PRPF8 dysregulation and their impact on cancer progression. We also discuss the emerging potential of targeting PRPF8 in cancer therapy, highlighting challenges in drug development.
Keywords: PRPF8; alternative splicing; cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- O’Grady L., Schrier Vergano S.A., Hoffman T.L., Sarco D., Cherny S., Bryant E., Schultz-Rogers L., Chung W.K., Sacharow S., Immken L.L., et al. Heterozygous variants in PRPF8 are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2022;188:2750–2759. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62772. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-Cánovas J.L., Hermán-Sánchez N., Del Rio-Moreno M., Fuentes-Fayos A.C., Lara-López A., Sánchez-Frias M.E., Amado V., Ciria R., Briceño J., de la Mata M., et al. PRPF8 increases the aggressiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating FAK/AKT pathway via fibronectin 1 splicing. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023;55:132–142. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00917-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials