Molecular Targets of 20-Hydroxyecdysone in Mammals, Mechanism of Action: Is It a Calorie Restriction Mimetic and Anti-Aging Compound?
- PMID: 40136680
- PMCID: PMC11941724
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14060431
Molecular Targets of 20-Hydroxyecdysone in Mammals, Mechanism of Action: Is It a Calorie Restriction Mimetic and Anti-Aging Compound?
Abstract
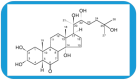
The 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) has been used in traditional medicine for a long time and acquired attention in the last decade as a food supplement and stimulant in physical activities. This polyhydroxylated cholesterol is found in the highest concentration in plants, and it is one of the secondary plant products that has a real hormonal influence in arthropods. Various beneficial effects have been reported in vivo and in vitro for 20E and its related compounds in mammals. Trials for the safety of clinical application showed a remarkably high tolerance in humans. This review aims to assess the latest development in the involvement of various pathways in tissues and organs and look if it is plausible to find a single primary target of this compound. The similarities with agents mimicking calorie restriction and anti-aging effects are also elucidated and discussed.
Keywords: 20-hydroxyecdysone; 20E; beta-ecdysone; ecdysterone.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dioh W., Tourette C., Del Signore S., Daudigny L., Dupont P., Balducci C., Dilda P.J., Lafont R., Veillet S. A Phase 1 study for safety and pharmacokinetics of BIO101 (20-hydroxyecdysone) in healthy young and older adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14:1259–1273. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13195. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lobo S.M., Plantefève G., Nair G., Cavalcante A.J., de Moraes N.F., Nunes E., Barnum O., Stadnik C.M.B., Lima M.P., Lins M., et al. Efficacy of oral 20-hydroxyecdysone (BIO101), a MAS receptor activator, in adults with severe COVID-19 (COVA): A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2024;68:102383. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102383. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

