Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) as Adjuvants in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- PMID: 40136683
- PMCID: PMC11941753
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14060434
Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) as Adjuvants in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Abstract
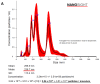
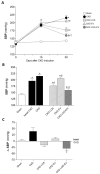
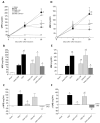
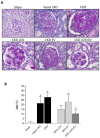
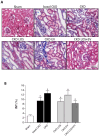
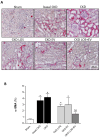
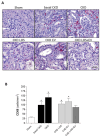
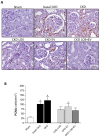
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is considered an important health issue worldwide. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockade through the administration of angiotensin II receptor blockers, such as Losartan (LOS), has been considered the best strategy for CKD treatment for decades. However, this approach promotes only partial detention of CKD progression and cannot reverse renal damage. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether the therapeutic administration of extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from adipose stem cells (ASCs), associated to LOS treatment, would promote additional renoprotection in rats underwent the 5/6 renal ablation CKD model. ASC-derived EV were administered locally, in the renal subcapsular area, 15 days after CKD induction, when LOS therapy also began. Animals were followed for additional 15 days and our results demonstrated that subcapsular injection of ASC-derived EV associated with LOS significantly reduced glomerulosclerosis, renal interstitial infiltration by myofibroblasts, and macrophages in the 5/6 CKD model. Additionally, LOS + EV abrogated systemic hypertension, proteinuria, and albuminuria, and stimulated local gene overexpression of the endogenous anti-inflammatory Il-4. Although more studies are still required to establish the best EV dose and administration route, these findings point to therapy with ASC-derived EV as a potential adjuvant in CKD treatment.
Keywords: cell therapy; chronic kidney disease; extracellular vesicles; mesenchymal stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Francis A., Harhay M., Ong A., Tummalapalli S.L., Fogo A.B., Fliser D., Roy-Chaudhury P., Fontana M., Nangaku M., Wanner C., et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: An international consensus. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024;20:1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vaidya S.R., Aeddula N.R. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Chronic Kidney Disease.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

