A Comprehensive Exploration of the Biological Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 40136706
- PMCID: PMC11941144
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14060458
A Comprehensive Exploration of the Biological Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
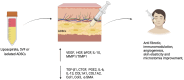
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by vasculopathy and tissue fibrosis affecting the skin and internal organs. Genetic and environmental factors influence susceptibility, severity, and onset. Current treatments are limited and not always effective, leading researchers to investigate new approaches, such as the use of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) through fat grafting. This review seeks to understand how ADSCs may impact the development and progression of SSc, with a particular focus on how these cells could alter immune responses and reduce fibrosis. ADSCs have been found to affect various immune cells, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, by releasing cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. These interactions generally suppress inflammation and promote a regulatory immune environment. Additionally, ADSCs can influence the extracellular matrix, helping to prevent fibrosis through signaling molecules like exosomes. ADSCs show promise as a treatment for SSc due to their ability to modulate the immune system and reduce fibrosis. Early clinical studies are encouraging, but more research is needed to fully understand how they work and to develop effective treatment protocols.
Keywords: ADSC; lipofilling; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Storti G., Scioli M.G., Kim B.-S., Terriaca S., Fiorelli E., Orlandi A., Cervelli V. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Adipose Tissue and Extracellular Vesicles in Ovarian Cancer Patients: A Bridge toward Metastatic Diffusion or a New Therapeutic Opportunity? Cells. 2021;10:2117. doi: 10.3390/cells10082117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

