Juglone-Bearing Thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazoles Induce Apoptosis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cells
- PMID: 40136714
- PMCID: PMC11941218
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14060465
Juglone-Bearing Thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazoles Induce Apoptosis in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
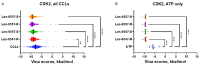
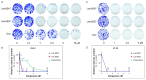
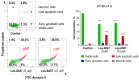
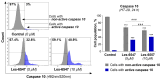
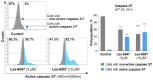
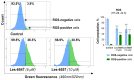
Colorectal cancer is a major global health challenge, with current treatments limited by toxicity and resistance. Thiazole derivatives, known for their bioactivity, are emerging as promising alternatives. Juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone) is a naturally occurring compound with known anticancer properties, and its incorporation into thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazole scaffolds may enhance their therapeutic potential. This study examined the cytotoxicity of thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazoles and their effects on apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Les-6547 and Les-6557 increased the population of ROS-positive HT-29 cancer cells approximately 10-fold compared with control cells (36.3% and 38.5% vs. 3.8%, respectively), potentially contributing to various downstream effects. Elevated ROS levels were associated with cell cycle arrest, inhibition of DNA biosynthesis, and reduced cell proliferation. A significant shift in the cell cycle distribution was observed, with an increase in S-phase (from 17.3% in the control to 34.7% to 51.3% for Les-6547 and Les-6557, respectively) and G2/M phase (from 24.3% to 39.9% and 28.8%). Additionally, Les-6547 and Les-6557 inhibited DNA biosynthesis in HT-29 cells, with IC50 values of 2.21 µM and 2.91 µM, respectively. Additionally, ROS generation may initiate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Les-6547 and Les-6557 activated both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways, demonstrated by notable increases in the activity of caspase 3/7, 8, 9, and 10. This study provides a robust basis for investigating the detailed molecular mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential of Les-6547 and Les-6557.
Keywords: apoptosis; colorectal cancer; proliferation; reactive oxygen species; thiopyrano[2,3-d]thiazoles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Bray F., Laversanne M., Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Menon G., Recio-Boiles A., Lotfollahzadeh S., Cagir B. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. [(accessed on 29 October 2024)]. Colon Cancer. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470380/
-
- Siegel R.L., Wagle N.S., Cercek A., Smith R.A., Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023;73:233–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

