Accessory Mental Foramina in Dry Mandibles: An Observational Study Along with Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40136722
- PMCID: PMC11941353
- DOI: 10.3390/dj13030094
Accessory Mental Foramina in Dry Mandibles: An Observational Study Along with Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
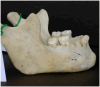
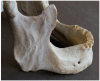
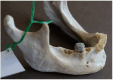
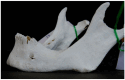
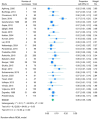
Background/Objectives: The mental foramen (MF) constitutes a passage for mental nerves and vessels, and it is a crucial anatomical landmark in the body of the mandible. The accessory mental foramen (AMF) is a small, addable foramen proximate to the MF, and it is mainly located posteriorly. The AMF is a rare anatomical variation in human mandibles that must be taken into consideration throughout dental and surgical operations. We aimed to assess the incidence and perform morphological and morphometric analyses of AMFs in the human dry mandibles of the Greek population, in addition to a relevant systematic review and meta-analysis of global data. Methods: We studied 114 human adult dry mandibles of unknown gender and age available from the Laboratory of Anatomy, Medical School, Democritus University of Thrace, Greece. We used the search term "accessory mental foramen" in the PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases to detect all publications of the last 50 years reporting the prevalence and morphology of AMFs in dry mandibles; the search ended on 13 January 2025. Quality assessments were performed using the relevant Joanna Briggs Institute tool. Data were synthesized with the random-effects REML model after Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformationusing STATA 18. No external funding was received. The PROSPERO CRD is 42025638135. Results: According to our data, the MF was present in all observed mandibles, and it was bilateral. Nine AMFs (five right/four left; five round/four oval; six posterior/three anterior to the MF) were found in seven mandibles (five single and two double), and all were unilateral. AMFs presented a mean diameter of 0.96 ± 0.43 mm and mean distances of 4.12 ± 2.15 mm from the MF, 12.68 ± 4.10 mm from the alveolar ridge, and 11.92 ± 1.57 mm from the lower border of the mandible. Furthermore, 27 publications were included in the meta-analysis; the combined AMF prevalence was 6.1% (95% CI: 4.8-7.6%; I2 60%), the combined mean vertical axis was 1.18 ± 0.61 mm, and the combined mean distance from the MF was 3.64 ± 2.29 mm. Bilateral AMFs were detected in 2.1% of AMF cases. An oval shape was described in 37.3% of AMFs. No publication bias was detected. Conclusions: AMFs are not considered rare, and they are occasionally bilateral or even multiple in number. Moreover, they demonstrate considerable variation regarding their size, shape, anddistance from the MF, alveolar ridge, and lower border of the mandible. Dental surgeons must be aware of AMFs' anatomical variations during surgical and anesthetic planning in order to effectively prevent or mitigate the risk of postoperative complications, such as pain, anesthesia, injury, and other adverse outcomes.
Keywords: Greek population; accessory mental foramen; mental foramen; meta-analysis; prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Almeida V.S.M., Bomfim R.T., Sobreira A.C.R., Barbosa I.D.S., Leite-Ribeiro P.M., Rubira-Bullen I.R., Sarmento V.A. Linear measurement accuracy of CBCT panoramic reconstructions: Experimental study with dry human mandibles. Oral Radiol. 2021;37:421–426. doi: 10.1007/s11282-020-00477-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

