Enhancing Root Canal Disinfection with Er:YAG Laser: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40136729
- PMCID: PMC11941447
- DOI: 10.3390/dj13030101
Enhancing Root Canal Disinfection with Er:YAG Laser: A Systematic Review
Abstract
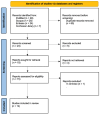
Background: The quest for minimally invasive disinfection in endodontics has led to using Erbium:Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet (Er:YAG) lasers. Conventional approaches may leave bacterial reservoirs in complex canal anatomies. Er:YAG's strong water absorption generates photoacoustic streaming, improving smear layer removal with lower thermal risk than other laser systems. Methods: This systematic review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Database searches (PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Library) identified studies (2015-2025) on Er:YAG laser-assisted root canal disinfection. Fifteen articles met the inclusion criteria: antibacterial efficacy, biofilm disruption, or smear layer removal. Data on laser settings, irrigants, and outcomes were extracted. The risk of bias was assessed using a ten-item checklist, based on guidelines from the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Results: All studies found Er:YAG laser activation significantly improved root canal disinfection over conventional or ultrasonic methods. Photon-induced photoacoustic streaming (PIPS) and shock wave-enhanced emission photoacoustic streaming (SWEEPS) yielded superior bacterial reduction, especially apically, and enabled lower sodium hypochlorite concentrations without sacrificing efficacy. Some research indicated reduced post-operative discomfort. However, protocols, laser parameters, and outcome measures varied, limiting direct comparisons and emphasizing the need for more standardized, long-term clinical trials. Conclusions: Er:YAG laser-assisted irrigation appears highly effective in biofilm disruption and smear layer removal, supporting deeper irrigant penetration. While findings are promising, further standardized research is needed to solidify guidelines and confirm Er:YAG lasers' long-term clinical benefits.
Keywords: Er:YAG laser; PIPS; SWEEPS; endodontics; photoacoustic streaming; root canal disinfection; smear layer removal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Hülsmann M. Effects of mechanical instrumentation and chemical irrigation on the root canal dentin. Endod. Top. 2013;29:55–86. doi: 10.1111/etp.12047. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous