Chronic Cavitary Pulmonary Histoplasmosis-Novel Concepts Regarding Pathogenesis
- PMID: 40137239
- PMCID: PMC11943228
- DOI: 10.3390/jof11030201
Chronic Cavitary Pulmonary Histoplasmosis-Novel Concepts Regarding Pathogenesis
Abstract
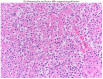
Because the apices of the lungs are most commonly involved in chronic cavitary histoplasmosis (CCPH), it has been assumed by many to have a pathogenesis which is similar to post-primary tuberculosis. Fungi such as Aspergillus may colonize pulmonary bullae. Although less common, colonization by Histoplasma capsulatum in a heavily endemic area is possible or even probable. In chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), apical bullae are characteristic. Since COPD is common and CCPH is rare, the pathogenesis of CCPH remains incompletely understood. What is presently known about the pathogenesis of CCPH has not changed appreciably since 1976. A cellblock from a patient with CCPH was analyzed with histochemical stains for T cells, B cells, plasma cells, and macrophages to better understand the pathogenesis of CCPH. The pathogenesis of cavitary disease in histoplasmosis has been assumed to resemble that of tuberculosis. However, liquefaction of a caseous focus in lung apices which resulted from blood-borne tubercle bacilli is distinctly unlike CCPH, as caseation is unusual. Rather, repeated colonization of the apical and other bullae by propagules (microconidium, macroconidium, hyphal fragment) of H. capsulatum in patients with COPD who have resided in heavily endemic areas appears to be the primary event in CCPH. Immunohistochemical enumeration of specific cell types in a patient with CCPH has not been previously carried out to our knowledge, but is only a first step in understanding the disease. In future studies, identification of the varieties of macrophages and cytokines in CCPH may reveal whether the process is pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, or both.
Keywords: cavitary; histoplasmosis; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kauffman C. Histoplasmosis. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 2003.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

