Hybridization Chain Reaction-Enhanced Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Analysis of miRNAs with a Silver Nano-Reporter on a Gold Nanostructured Electrode Array
- PMID: 40137377
- PMCID: PMC11943109
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb16030098
Hybridization Chain Reaction-Enhanced Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Analysis of miRNAs with a Silver Nano-Reporter on a Gold Nanostructured Electrode Array
Abstract
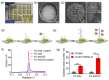
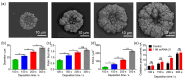
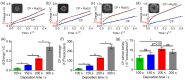
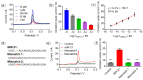
Abnormal expression of miRNAs is associated with the occurrence and progression of cancer and other diseases, making miRNAs essential biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis. However, the intrinsic properties of miRNAs, such as short length, low abundance, and high sequence homology, represent great challenges for fast and accurate miRNA detection in clinics. Herein, we developed a novel hybridization chain reaction (HCR)-based electrochemical miRNAs chip (e-miRchip), featured with gold nanostructured electrodes (GNEs) and silver nanoparticle reporters (AgNRs), for sensitive and multiplexed miRNA detection. AgNRs were synthesized and applied on the e-miRchip to generate strong redox signals in the presence of miRNA. The stem-loop capture probe was covalently immobilized on the GNEs, and was opened upon miRNA hybridization to consequently trigger the HCR for signal amplification. The multiple long-repeated DNA helix generated by HCR provides the binding sites for the AgNRs, contributing to the amplification of the electrochemical signals of miRNA hybridization. To optimize the detection sensitivity, GNEs with three distinct structures were electroplated, in which flower-like GNEs were found to be the best electrode morphology for miRNAs analysis. Under optimal conditions, the HCR-based e-miRchip showed an excellent detection performance with an LOD of 0.9 fM and a linear detection range from 1 fM to 10 pM. Moreover, this HCR-based e-miRchip platform was able to effectively distinguish miRNAs from the one- or two-base mismatches. This HCR-based e-miRchip holds great potential as a highly efficient and promising miRNA detection platform for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and other diseases in the future.
Keywords: HCR; electrochemical detection; miRNAs; nanostructured electrode; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Silver nano-reporter enables simple and ultrasensitive profiling of microRNAs on a nanoflower-like microelectrode array on glass.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Oct 23;20(1):456. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01664-7. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36274120 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-signal amplification electrochemical sensing for the sensitive detection of uranyl ion based on gold nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction-assisted synthesis of silver nanoclusters.Anal Chim Acta. 2021 Nov 1;1184:338986. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.338986. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Anal Chim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34625249
-
Exponential rolling circle amplification-hybridization chain reaction (EXRCA-HCR) for AgNPs@gel-enhanced fluorescence ultrasensitive detection of miRNA-21.Anal Chim Acta. 2025 Jul 8;1358:344095. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2025.344095. Epub 2025 Apr 19. Anal Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40374247
-
An enzyme-free electrochemical sandwich DNA assay based on the use of hybridization chain reaction and gold nanoparticles: application to the determination of the DNA of Helicobacter pylori.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Dec 20;187(1):73. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3999-z. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31863213
-
Bifunctional Y-shaped probe combined with dual amplification for colorimetric sensing and molecular logic operation of two miRNAs.Talanta. 2023 Jul 1;259:124480. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124480. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 37004396
References
-
- Sidorova E.A., Zhernov Y.V., Antsupova M.A., Khadzhieva K.R., Izmailova A.A., Kraskevich D.A., Belova E.V., Simanovsky A.A., Shcherbakov D.V., Zabroda N.N., et al. The Role of Different Types of microRNA in the Pathogenesis of Breast and Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:1980. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031980. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

