Intrauterine Zika Virus Infection: An Overview of the Current Findings
- PMID: 40137414
- PMCID: PMC11943202
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm15030098
Intrauterine Zika Virus Infection: An Overview of the Current Findings
Abstract
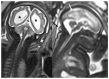
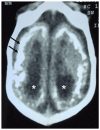
Zika virus (ZIKV) is a mosquito-borne flavivirus of the family Flaviviridae. The association between ZIKV and microcephaly was first described in Brazil in 2015. The risk of vertical transmission occurs in pregnant women with or without symptoms, and the risk of malformation appears to be worse when infection occurs in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. The rate of vertical transmission varies from 26 to 65%, and not all fetuses develop malformations. The incidence of malformations resulting from transmission is uncertain, ranging from 6-8% in the US to 40% in Brazil. Congenital ZIKV syndrome is a set of clinical manifestations that can affect the fetus of a mother infected with ZIKV. The manifestations are broad and nonspecific, including microcephaly, subcortical calcifications, ocular changes, congenital contractures, early hypertension, and pyramidal and extrapyramidal signs. Other findings such as growth restriction and fetal miscarriage/death may also occur. Our aim in this article is to review the literature on mosquito transmission, clinical presentation, serologic diagnosis, intrauterine transmission, pre- and postnatal imaging diagnostic findings, and short- and long-term follow-up.
Keywords: Zika virus; fetal malformations; imaging diagnostic methods; intrauterine infection; pregnancy; vertical infectious disease transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Werner H., Sodré D., Hygino C., Guedes B., Fazecas T., Nogueira R., Daltro P., Tonni G., Lopes J., Araujo Júnior E. First-trimester intrauterine Zika virus infection and brain pathology: Prenatal and postnatal neuroimaging findings. Prenat. Diagn. 2016;36:785–789. doi: 10.1002/pd.4860. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

