Comparative Assessment of Short- and Long-Term Effects of Triadimenol Fungicide on Danio rerio Erythrocytes Using the Micronucleus and Erythrocyte Nuclear Abnormality Assays
- PMID: 40137526
- PMCID: PMC11946059
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13030199
Comparative Assessment of Short- and Long-Term Effects of Triadimenol Fungicide on Danio rerio Erythrocytes Using the Micronucleus and Erythrocyte Nuclear Abnormality Assays
Abstract
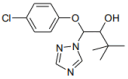
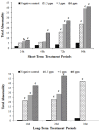
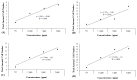
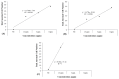
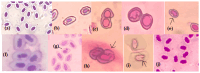
Triadimenol is a systemic fungicide widely used in agriculture to manage plant diseases, especially fungal infections. This study aims to evaluate the short-term (24, 48, 72 and 96 h) and long-term (10, 20, and 30 days) genotoxic effects of different concentrations of triadimenol on zebrafish (Danio rerio) erythrocytes using micronucleus (MN) and erythrocyte nuclear abnormal (ENA) assay. Fish were treated with 1.5, 3, and 6 mg/L concentrations of triadimenol for short and long-term periods. After the treatment period, blood was collected with heparin syringe, smears were prepared, the preparations were fixed and stained. For MN assay in short-term treatments, statistically significant MN formation was found at all concentrations of triadimenol for 24 h treatment, at the highest triadimenol concentration for 48 h, at 1.5 and 3 mg/L concentrations for 72 h, and at 3 mg/L concentrations for 96 h, compared to the negative control. In long-term treatments, significant increases in MN formation were observed at all concentrations of triadimenol for 10 and 20 days of treatment compared to the negative control. Mortality occurred at 3 and 6 mg/L concentrations in the 30-day treatment. The most frequently detected abnormalities included echinocytes and binuclear cells. For ENA assay, abnormalities such as echinocytes, binuclear cells, segmented cells, and kidney-shaped nuclei were detected in fish erythrocytes treated with different concentrations of triadimenol. All concentrations of triadimenol caused an increase in the total abnormality level in Danio rerio erythrocytes at all treatment times. These increases were concentration dependent for both short-term and long-term treatments. In conclusion, this study emphasized the potential genotoxic risks of triadimenol fungicide for aquatic organisms in both short-term and long-term treatments and the need for further ecotoxicological evaluation.
Keywords: ecotoxicology; genotoxicity; genotoxicity assays; triadimenol; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Determination of micronuclei frequency in Danio rerio for assessing genotoxicity induced by propineb.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2024 Nov;47(6):848-853. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2024.2303970. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38225881
-
Erythrocyte alterations in specimens of Danio rerio caused by exposure to metformin.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;106:104373. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2024.104373. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38244880
-
The role of vitamins A, C, E and selenium as antioxidants against genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on erythrocytes of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2014 Jun;104:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.02.015. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2014. PMID: 24632120
-
Micronucleus test and nuclear abnormality assay in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Past, present, and future trends.Environ Pollut. 2021 Dec 1;290:118019. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118019. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Environ Pollut. 2021. PMID: 34670334 Review.
-
Micronucleus assay in aquatic animals.Mutagenesis. 2011 Jan;26(1):205-13. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geq073. Mutagenesis. 2011. PMID: 21164204 Review.
References
-
- FAOSTAT, 2020. Pesticides Use. [(accessed on 18 February 2025)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RP.
-
- How C.M., Li S.W., Liao V.H. Chronic exposure to triadimenol at environmentally relevant concentration adversely affects aging biomarkers in Caenorhabditis elegans associated with insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2018;640–641:485–492. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.314. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Unal F., Demir H., Yuzbasioglu D. Genotoxic effects of environmental contaminant methidathion and triadimenol pesticides; Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on EuroAsian Biodiversity; Minsk, Belarus. 5–8 July 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

