Thalassophryne maculosa (Batrachoididae: Thalassophryninae) as a Bioindicator of Mercury-Induced Genotoxicity
- PMID: 40137533
- PMCID: PMC11946055
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13030206
Thalassophryne maculosa (Batrachoididae: Thalassophryninae) as a Bioindicator of Mercury-Induced Genotoxicity
Abstract
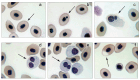
Environmental monitoring requires reliable bioindicators to assess the genotoxic effects of pollutants in aquatic ecosystems. In this study, the marine fish Thalassophryne maculosa was evaluated as a bioindicator of genotoxicity through the application of the micronucleus test. Fish were exposed to varying concentrations of mercuric chloride (HgCl2) (0.1, 0.25, and 0.5 µg HgCl2/g body weight) over different time intervals (24, 48, 72, and 96 h). A dose- and time-dependent increase in nuclear abnormalities, including micronuclei, was observed, with significant chromosomal damage detected at 0.25 and 0.5 µg HgCl2/g body weight. These results demonstrate the sensitivity of T. maculosa to mercury exposure, even at concentrations below regulatory safety thresholds, emphasizing its suitability as a bioindicator for detecting genotoxic contamination in coastal ecosystems. This study provides critical insights into the ecological risks posed by mercury and highlights the potential of T. maculosa to enhance environmental monitoring programs, particularly in regions vulnerable to heavy metal pollution.
Keywords: Thalassophryne maculosa; bioindicator; genotoxicity; marine pollution; mercury; micronuclei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bashir I., Lone F.A., Bhat R.A., Mir S.A., Dar Z.A., Dar S.A. Concerns and Threats of Contamination on Aquatic Ecosystems. In: Hakeem K.R., Bhat R.A., Qadri H., editors. Bioremediation and Biotechnology: Sustainable Approaches to Pollution Degradation. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2020. pp. 1–26.
-
- Edo G.I., Itoje-akpokiniovo L.O., Obasohan P., Ikpekoro V.O., Samuel P.O., Jikah A.N., Nosu L.C., Ekokotu H.A., Ugbune U., Oghroro E.E.A., et al. Impact of Environmental Pollution from Human Activities on Water, Air Quality and Climate Change. Ecol. Front. 2024;44:874–889. doi: 10.1016/j.ecofro.2024.02.014. - DOI
-
- Rashid A., Schutte B.J., Ulery A., Deyholos M.K., Sanogo S., Lehnhoff E.A., Beck L. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Soil: Environmental Pollutants Affecting Crop Health. Agronomy. 2023;13:1521. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13061521. - DOI
-
- De Marco A., Proietti C., Anav A., Ciancarella L., D’Elia I., Fares S., Fornasier M.F., Fusaro L., Gualtieri M., Manes F., et al. Impacts of Air Pollution on Human and Ecosystem Health, and Implications for the National Emission Ceilings Directive: Insights from Italy. Environ. Int. 2019;125:320–333. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.064. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singh R., Verma A.K., Prakash S. The Web of Life: Role of Pollution in Biodiversity Decline. Int. J. Fauna Biol. Stud. 2023;10:49–52. doi: 10.22271/23940522.2023.v10.i3a.1003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

