The Effects of Air Pollution on Neurological Diseases: A Narrative Review on Causes and Mechanisms
- PMID: 40137534
- PMCID: PMC11946816
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13030207
The Effects of Air Pollution on Neurological Diseases: A Narrative Review on Causes and Mechanisms
Abstract
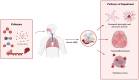
Air pollution has well-documented adverse effects on human health; however, its impact on neurological diseases remains underrecognized. The mechanisms by which various components of air pollutants contribute to neurological disorders are not yet fully understood. This review focuses on key air pollutants, including particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO), and diesel exhaust particles (DEPs). This paper summarizes key findings on the effects of air pollution on neurological disorders, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), and Parkinson's disease (PD). Although the precise biological mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated, evidence suggests that multiple pathways are involved, including blood-brain barrier disruption, oxidative stress, inflammation, and the activation of microglia and astrocytes. This review underscores the role of environmental pollutants as significant risk factors for various neurological diseases and explores their mechanisms of action. By advancing our understanding of these interactions, this work aims to inform new insights for mitigating the adverse effects of air pollution on neurological diseases, ultimately contributing to the establishment of a cleaner and healthier environment for future generations.
Keywords: air pollution; inflammation; neurological diseases; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources