The Association Between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Thyroid Hormones in Men and Non-Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40137541
- PMCID: PMC11946724
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13030214
The Association Between Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Exposure and Thyroid Hormones in Men and Non-Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
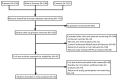
Studies have shown that per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) may impact thyroid function in human health. While the consistency between PFAS exposure and thyroid health effects in pregnant women has been validated, the effects on men and non-pregnant women remains inconclusive. To address this, a meta-analysis was carried out in this paper, with 14 eligible studies retrieved from Embase, PubMed, and Web of Science that were published up to 2 June 2024, focusing on the relationship between PFAS exposure and its effect on thyroid hormone levels in the human body. The thyroid function indexes analyzed included thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), free T3 (FT3), and free T4 (FT4). The estimated value (β) and the corresponding confidence interval (95% CI) were extracted from the literature. A heterogeneity test was carried out, and the sensitivity analysis and publication bias of the studies were analyzed using Stata 18.0. The results revealed that in men and non-pregnant women, PFOA was positively correlated with FT3 (β = 0.011, 95% CI = 0.001, 0.02, I2 = 13.4). However, no significant associations were found between exposure to other PFAS and thyroid hormones. A subgroup analysis further indicated that the correlations between PFAS exposure and thyroid hormone levels were more significant in adolescents, in both America and Europe.
Keywords: meta-analysis; non-pregnant women; per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances; thyroid hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
Chaofei Li, Sha Li and Yanying Chen are employed by Zhonghuan (Fujian) Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. Yu Qiu is employed by Fujian Jinhuang Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd. They declare no conflict of interest with Bin Zhang, Meizi Zhao, Xiangru Cong, Chunyu Liu, Xiaoxue Li and Penghui Li.
Figures


References
-
- Sun Y., Teng D., Zhao L., Shi X.G., Li Y.Z., Shan Z.Y., Teng W.P., Thyroid Disorders, Iodine Status and Diabetes Epidemiological Survey Group (TIDE) Impaired Sensitivity to Thyroid Hormones Is Associated with Hyperuricemia, Obesity, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Subjects with Subclinical Hypothyroidism. Thyroid. 2022;32:376–384. doi: 10.1089/thy.2021.0500. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

