Assessing the Impact of Aviation Emissions on Air Quality at a Regional Greek Airport Using Machine Learning
- PMID: 40137544
- PMCID: PMC11945904
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13030217
Assessing the Impact of Aviation Emissions on Air Quality at a Regional Greek Airport Using Machine Learning
Abstract
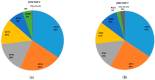
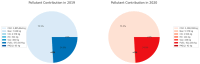
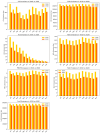
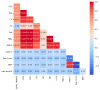
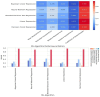
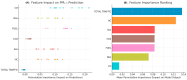
Aviation emissions significantly impact air quality, contributing to environmental degradation and public health risks. This study aims to assess the impact of aviation-related emissions on air quality at Alexandroupolis Regional Airport, Greece, and evaluate the role of meteorological factors in pollution dispersion. Using machine learning models, we analyzed emissions data, including CO2, NOx, CO, HC, SOx, PM2.5, fuel consumption, and meteorological parameters from 2019-2020. Results indicate that NOx and CO2 emissions showed the highest correlation with air traffic volume and fuel consumption (R = 0.63 and 0.67, respectively). Bayesian Linear Regression and Linear Regression emerged as the most accurate models, achieving an R2 value of 0.96 and 0.97, respectively, for predicting PM2.5 concentrations. Meteorological factors had a moderate influence, with precipitation negatively correlated with PM2.5 (-0.03), while temperature and wind speed showed limited effects on emissions. A significant decline in aviation emissions was observed in 2020, with CO2 emissions decreasing by 28.1%, NOx by 26.5%, and PM2.5 by 35.4% compared to 2019, reflecting the impact of COVID-19 travel restrictions. Carbon dioxide had the most extensive percentage distribution, accounting for 75.5% of total emissions, followed by fuels, which accounted for 24%, and the remaining pollutants, such as NOx, CO, HC, SOx, and PM2.5, had more minor impacts. These findings highlight the need for optimized air quality management at regional airports, integrating machine learning for predictive monitoring and supporting policy interventions to mitigate aviation-related pollution.
Keywords: air pollution; airport; environment; gas emission; health; machine learning models; public health; transport.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Ioannis Manisalidis was employed by the company Delphis S.A. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu J., Attari M.U., Akhtar M., Amin M., Yu Z., Janjua L. Investigating the Impact of Transport Services and Renewable Energy on Macro-Economic and Environmental Indicators. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022;10:916176. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.916176. - DOI
-
- European Environment Agency Air Pollution. [(accessed on 21 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

