Sensitivity of Immunodiagnostic Tests in Localized Versus Disseminated Tuberculosis-A Systematic Review of Individual Patient Data
- PMID: 40137824
- PMCID: PMC11946558
- DOI: 10.3390/tropicalmed10030070
Sensitivity of Immunodiagnostic Tests in Localized Versus Disseminated Tuberculosis-A Systematic Review of Individual Patient Data
Abstract
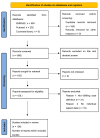
Our objective was to perform a systematic review of individual patient data comparing immunodiagnostic test sensitivity in patients with localized versus disseminated tuberculosis who are from high- and less-than-high-income countries. In a systematic review of individual patient data, we compared IGRA results and characteristics of patients with disseminated tuberculosis with IGRA results and characteristics of patients with localized tuberculosis. Data were extracted from Pubmed, EMBASE and the Cochrane Library, analyzed and presented following the PRISMA-IPD and STROBE statements. We identified 52 patients with localized and 105 with disseminated tuberculosis. Immunodiagnostic tests in localized tuberculosis from high-income countries were positive in 88.8% and in 67.3% of patients with disseminated tuberculosis (p = 0.034). In patients from less-than-high-income countries, the sensitivity of immunodiagnostic tests was not significantly lower with disseminated tuberculosis. Patients with disseminated tuberculosis were significantly younger and had a higher rate of microbiological confirmation. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that rate of microbiological confirmation was associated with a negative IGRA. Disseminated tuberculosis may be associated with a reduced sensitivity of IGRA in high-income countries and this may be related to a higher bacterial load with a negative IGRA.
Keywords: interferon gamma release assay; lymph node tuberculosis; miliary tuberculosis; sensitivity; tuberculous meningitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Roy R.B., Thee S., Blázquez-Gamero D., Falcón-Neyra L., Neth O., Noguera-Julian A., Lillo C., Galli L., Venturini E., Buonsenso D., et al. Performance of immune-based and microbiological tests in children with tuberculosis meningitis in Europe: A multicentre Paediatric Tuberculosis Network European Trials Group (ptbnet) study. Eur. Respir. J. 2020;56:1902004. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martínez-Planas A., Baquero-Artigao F., Santiago B., Fortuny C., Méndez-Echevarría A., Del Rosal T., Bustillo-Alonso M., Gale I., Guerrero C., Blázquez-Gamero D., et al. Interferon-Gamma Release Assays Differentiate between Mycobacterium avium Complex and Tuberculous Lymphadenitis in Children. J. Pediatr. 2021;236:211–218. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liao C.H., Chou C.H., Lai C.C., Huang Y.T., Tan C.K., Hsu H.L., Hsueh P.R. Diagnostic performance of an enzyme-linked immunospot assay for interferon-gamma in extrapulmonary tuberculosis varies between different sites of disease. J. Infect. 2009;59:402–408. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2009.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources