Systemic immunomodulation by irreversible electroporation versus stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: the CROSSFIRE trial
- PMID: 40139834
- PMCID: PMC11950998
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010222
Systemic immunomodulation by irreversible electroporation versus stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: the CROSSFIRE trial
Abstract
Background: Irreversible electroporation (IRE) and stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy (SABR) are cytoreductive therapies for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC). Both may signify immunogenic cell death. We aimed to compare systemic immune responses between the treatments.
Methods: As part of the randomized phase II CROSSFIRE trial (NCT02791503), comparing the oncological efficacy of IRE to SABR in patients with LAPC, pre- and post-treatment (2 weeks and 3 months) peripheral blood samples were collected. Frequency and activation status of lymphocytic and myeloid subsets were determined using flow cytometry. T cell responses to pancreatic cancer associated with Wilms tumor-1 (WT-1) and survivin tumor antigens were determined by interferon-γ enzyme-linked immunospot assay.
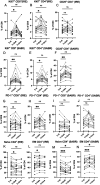
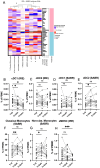
Results: In total, 20 IRE and 20 SABR-treated participants were analyzed (20 men; median age 65 (IQR 55-70)). IRE induced immediate decreases in systemic regulatory T cell (Treg) and conventional type-1 dendritic cell rates, coinciding with CD4+/CD8+ T cell activation by upregulation of PD-1, which was associated with improved overall survival (OS). SABR similarly induced immediate CD4+/CD8+ T cell activation by upregulation of Ki67 and CD25 but resulted in asynchronously delayed Treg downregulation. SABR also induced a durable increase in CD4+ EM T cells, associated with improved OS. Ablation-induced WT-1 or survivin-specific T cell responses were observed in 9/16 (56%) immune competent participants (IRE n=5, SABR n=4) and were associated with longer OS.
Conclusion: Distinct immune stimulatory responses associated with improved OS, suggest that SABR might benefit from combined Treg depletion strategies while IRE could benefit from PD-1 checkpoint inhibition.
Trial registration number: The trial was registered on clinical trials.gov (NCT02791503).
Keywords: Abscopal; Adenocarcinoma; Immune modulatory.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MM is a paid consultant for Angio Dynamics, editor for Springer’s journal of Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology, and founder and director of MedPeers. HS, FEFT, and BG received research funding from Angio Dynamics for the conduct of the PANFIRE I/II and III trials and CROSSFIRE trial. TDdG received research funding from Idera Pharmaceuticals and Glycostem and consultancy fees from LAVA Therapeutics, GE Health and Mendus. AR, DV, JB, MD, SML, RB, SN, BB, ES, PvdT, RP, and JdV have no relevant competing interests to declare.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
