EPA Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Transcriptome in T Cells, Implicating a Triglyceride-Independent Pathway in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
- PMID: 40139879
- PMCID: PMC12013851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2024.09.002
EPA Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Transcriptome in T Cells, Implicating a Triglyceride-Independent Pathway in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
Abstract
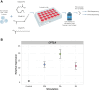
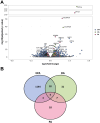
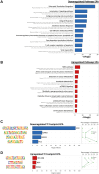
Twice-daily intake of purified eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) reduces atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in patients with high triglycerides, but its exact mechanism remains unclear. We exposed non-activated CD4+ T cells to 100μM EPA, oleic acid, palmitic acid, or control, and conducted RNA and ATAC-sequencing after 48 hours. EPA exposure downregulated immune response-related genes like HLA-DRA, CD69, and IL2RA, and upregulated oxidative stress prevention genes like NQO1. Transcription factor footprinting showed decreased GATA3 and PU.1, and increased REV-ERB. These effects were specific to EPA, suggesting it induces an anti-inflammatory transcriptomic landscape in CD4+ T cells, contributing to its observed cardiovascular benefits.
Keywords: T cells; atherosclerosis; eicosapentaenoic acid; oleic acid; palmitic acid; transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding Support and Author Disclosures The authors’ work is supported by the Dutch Cardiovascular Alliance (Dutch Heart Foundation, Dutch Federation of University Medical Centers, Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and Royal Netherlands Academy of Sciences) for the GENIUSII project Generating the Best Evidence-Based Pharmaceutical Targets for Atherosclerosis (CVON2017-20). The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Lawler P.R., Bhatt D.L., Godoy L.C., et al. Targeting cardiovascular inflammation: next steps in clinical translation. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(1):113–131. - PubMed
-
- Sabatine M.S., Giugliano R.P., Keech A.C., et al. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(18):1713–1722. - PubMed
-
- Schade D.S., Eaton R.P. Residual cardiovascular risk—is inflammation the primary cause? World J Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;8(1):59–69.
-
- Lawler P.R., Kotrri G., Koh M., et al. Real-world risk of cardiovascular outcomes associated with hypertriglyceridaemia among individuals with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and potential eligibility for emerging therapies. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(1):86–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

