Outcomes in patients with classic Hodgkin lymphoma refractory or intolerant to brentuximab vedotin and anti-PD-1 therapy: a real world analysis from 15 U.S. academic centers
- PMID: 40140364
- PMCID: PMC11947194
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-025-01257-1
Outcomes in patients with classic Hodgkin lymphoma refractory or intolerant to brentuximab vedotin and anti-PD-1 therapy: a real world analysis from 15 U.S. academic centers
Abstract
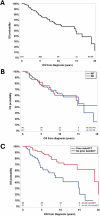
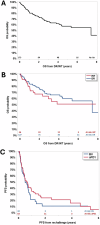
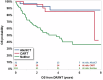
Anti-PD-1 based therapies and brentuximab vedotin (BV) have significantly improved survival in patients with classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) and have been incorporated into earlier lines of therapy. However, there is insufficient data regarding the clinical outcomes in patients who develop refractory disease or who become intolerant of BV and anti-PD-1 therapies (double refractory/intolerant; DR/INT). Here, we evaluated outcomes in patients with DR/INT cHL from 15 US academic medical centers. A total of 173 patients were identified as DR/INT. The median overall survival from the time of cHL diagnosis (OS-1) was 14.8 years (95% CI: 10.9-20.9 years) and the 10-year OS-1 estimate was 62% (95% CI: 52-70%). After accounting for differences in age, patients who underwent autologous stem cell transplant prior to developing DR/INT had significantly longer OS-1 (HR 0.53, 95% CI: 0.29-0.96, p = 0.04). Median OS from time of DR/INT (OS-2) was 7.4 years (95% CI: 4.3-NR) and the 5-year OS-2 estimate was 57% (95% CI: 48-66%). Both anti-PD-1 and BV based therapy rechallenge were effective with median PFS of 237 days (95% CI: 155-357 days) and 183 days (95% CI: 108-273 days), respectively. Finally, advanced therapy options such as CD30 directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy and allogeneic stem cell transplant after DR/INT were associated with improved OS-2 (p < 0.001). To our knowledge, this represents the largest cohort of patients with DR/INT cHL. OS-2 will serve as a benchmark for future studies aiming to improve survival in DR/INT cHL.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: NE: Research funding: Beigene, Lilly, and Incyte; Speakers Bureau for Beigene and Genentech, Ad boards for ADC Therapeutics, Lilly, and Ipsen; Honorarium from Novartis. TJV: Advisory Board: Genmab/AbbVie, ADC Therapeutics. Consultancy: Novartis, Recordati, Genmab. Research Funding: Kite, Viracta, Incyte/Morphosys, Genmab/AbbVie, Recordati. TKM: Advisory Board: Kite. Research funding: Genmab, Century Therapeutics, Johnson & Johnson. PRG: Consultancy: Kite/Gilead Pharma, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS). Advisory Board ADC Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Cellectar Biosciences, Ono Pharma, Ipsen Biopharma and Regeneron Pharma. SS: Advisory Board ADC Therapeutics. CD: Advisory Board: EMD Serono Advisory Board, Cogent Biosciences. Ethics approval: This retrospective study approved through The Ohio State University institutional review board (Study Number: 2022C0159). Given the retrospective nature of this study, individual patient consent was waived and de-identified data was utilized for analysis. The study was conducted in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Figures
References
-
- Ansell SM. Hodgkin lymphoma: 2018 update on diagnosis, risk‐stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2018;93:704–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

