Shared early molecular mechanisms revealed in P301S and 5xFAD Alzheimer's disease mouse models
- PMID: 40140365
- PMCID: PMC11947184
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03321-7
Shared early molecular mechanisms revealed in P301S and 5xFAD Alzheimer's disease mouse models
Abstract
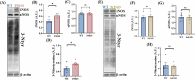
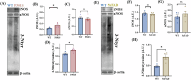
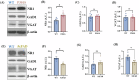
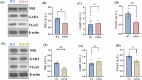
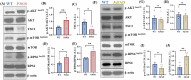
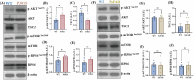
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by early molecular events that influence disease progression. Still, the molecular mechanisms caused by different mutations of AD are not understood. We have performed a multidisciplinary study to investigate and compare the early stages of the pathology in two transgenic AD mouse models: P301S and 5xFAD. Using SNOTRAP-based mass spectrometry, we assessed changes in S-nitrosylation, a nitric oxide-mediated post-translational modification, of proteins in both models during their juvenile age. The increased levels of 3-nitrotyrosine confirmed nitrosative stress in the mutant mice. Systems biology analysis revealed shared processes between the models, particularly in the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission processes. In the P301S model, we identified 273 S-nitrosylated (SNOed) proteins in the cortex, with 244 proteins uniquely SNOed in the diseased mice. In the 5xFAD model, 309 SNOed proteins were identified. We have found altered proteins expression of different glutamate/GABA-related markers in the cortex and hippocampus of both AD mouse models. Additionally, the phosphorylation levels of the mTOR signaling components revealed hyperactivation of this pathway in P301S mice. Conversely, 5xFAD mice showed no significant changes in mTOR signaling except for elevated phosphorylation of the ribosomal protein S6 in the cortex. Our findings revealed key molecular mechanisms in the two AD mouse models during their early stages. These mechanisms could serve as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for early-stage AD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HA is a CSO of Point6 Bio and Neuro-NOS. No funds from both companies were received for this study. All other authors do not hold any competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hippocampal disruptions of synaptic and astrocyte metabolism are primary events of early amyloid pathology in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 16;12(11):954. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04237-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34657143 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct and Convergent Alterations of Entorhinal Cortical Circuits in Two Mouse Models for Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;98(3):1121-1131. doi: 10.3233/JAD-231413. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38489190 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of the hippocampus in the 5XFAD mouse model at early stages of Alzheimer's disease pathology.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;36(2):321-34. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130311. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23603400
-
The behavioural and neuropathologic sexual dimorphism and absence of MIP-3α in tau P301S mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Feb 24;17(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01749-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32093751 Free PMC article.
-
Hearing modulation affects Alzheimer's disease progression linked to brain inflammation: a study in mouse models.Mol Med. 2024 Dec 26;30(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-01040-1. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39725872 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of S6K1 in Aging and Alzheimer's Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5923. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135923. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649702 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zvěřová M. Clinical aspects of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Biochem. 2019;72:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Kuslansky G, Buschke H, Katz M, Sliwinski M, Lipton RB. Screening for Alzheimer’s disease: the memory impairment screen versus the conventional three‐word memory test. J Am Geriatrics Soc. 2002;50:1086–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

