Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals potential therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40140461
- PMCID: PMC11947091
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-93916-3
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals potential therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment of lung squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
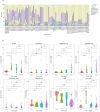
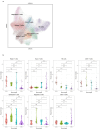
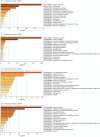
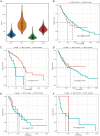
Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), accounting for 30% of lung cancer cases, lacks adequate research due to limited understanding of its molecular abnormalities. Our study analyzed public LUSC datasets to explore the tumor microenvironment (TME) composition using scRNA-seq from two cohorts. Applying non-negative matrix factorization, we identified unique malignant cell phenotypes, or meta-programs (MPs), based on gene expression patterns. Survival analysis revealed the clinical relevance of these MPs. Findings illuminated a TME landscape enriched with immune cells-CD8 + T, exhausted T, CD4 + T, and naive T cells-and suggested roles for myeloid cells, like cDC1 and pDCs, in LUSC progression. Different MPs highlighted the heterogeneity of malignant cells and their clinical implications. Targeting MP-specific genes may enable personalized therapy, especially for early-stage LUSC. This study offers insights into immune cell function in tumor dynamics, identifies MPs, and paves the way for novel LUSC strategies, enhancing early intervention, personalized treatment, and prognosis, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Lung cancer; Non-negative matrix factorization; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.68 (6), 394–424 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Herbst, R. S., Morgensztern, D. & Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature553 (7689), 446–454 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Chen, S. et al. Introduction of exogenous wild–type p53 mediates the regulation of oncoprotein 18/stathmin signaling via nuclear factor–κB in non–small cell lung cancer NCI–H1299 cells. Oncol. Rep.41 (3), 2051–2059 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Yang, M. et al. A multi-omics machine learning framework in predicting the survival of colorectal cancer patients. Comput. Biol. Med.146, 105516 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

