A coronavirus assembly inhibitor that targets the viral membrane protein
- PMID: 40140569
- PMCID: PMC11981944
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08773-x
A coronavirus assembly inhibitor that targets the viral membrane protein
Abstract
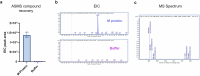
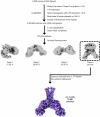
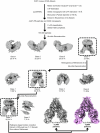
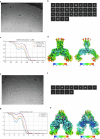
The coronavirus membrane protein (M) is the main organizer of coronavirus assembly1-3. Here, we report on an M-targeting molecule, CIM-834, that blocks the assembly of SARS-CoV-2. CIM-834 was obtained through high-throughput phenotypic antiviral screening followed by medicinal-chemistry efforts and target elucidation. CIM-834 inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 (including a broad panel of variants) and SARS-CoV. In SCID mice and Syrian hamsters intranasally infected with SARS-CoV-2, oral treatment reduced lung viral titres to nearly undetectable levels, even (as shown in mice) when treatment was delayed until 24 h before the end point. Treatment of infected hamsters prevented transmission to untreated sentinels. Transmission electron microscopy studies show that virion assembly is completely absent in cells treated with CIM-834. Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy reveals that CIM-834 binds and stabilizes the M protein in its short form, thereby preventing the conformational switch to the long form, which is required for successful particle assembly. In conclusion, we have discovered a new druggable target in the replication cycle of coronaviruses and a small molecule that potently inhibits it.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KU Leuven has filed a patent application claiming the discovery of a class of antiviral molecules to which CIM-834 belongs as SARS-CoV-2 replication inhibitors. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Our World in Data. Estimated cumulative excess deaths per 100,000 people during COVID-19, Jun17, 2024. https://ourworldindata.org/explorers/coronavirus-data-explorer.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

