Plasticity of the mammalian integrated stress response
- PMID: 40140574
- PMCID: PMC12119373
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08794-6
Plasticity of the mammalian integrated stress response
Abstract
An increased level of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit-α (eIF2α, encoded by EIF2S1; eIF2α-p) coupled with decreased guanine nucleotide exchange activity of eIF2B is a hallmark of the 'canonical' integrated stress response (c-ISR)1. It is unclear whether impaired eIF2B activity in human diseases including leukodystrophies2, which occurs in the absence of eIF2α-p induction, is synonymous with the c-ISR. Here we describe a mechanism triggered by decreased eIF2B activity, distinct from the c-ISR, which we term the split ISR (s-ISR). The s-ISR is characterized by translational and transcriptional programs that are different from those observed in the c-ISR. Opposite to the c-ISR, the s-ISR requires eIF4E-dependent translation of the upstream open reading frame 1 and subsequent stabilization of ATF4 mRNA. This is followed by altered expression of a subset of metabolic genes (for example, PCK2), resulting in metabolic rewiring required to maintain cellular bioenergetics when eIF2B activity is attenuated. Overall, these data demonstrate a plasticity of the mammalian ISR, whereby the loss of eIF2B activity in the absence of eIF2α-p induction activates the eIF4E-ATF4-PCK2 axis to maintain energy homeostasis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: E.J. is an employee of and holds equity in Moderna Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
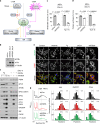
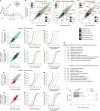
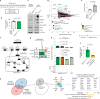

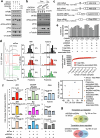
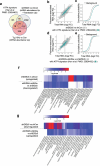
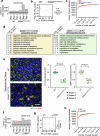
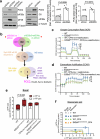
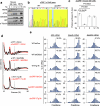
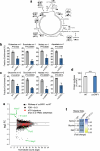


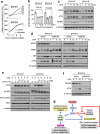
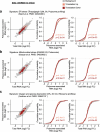
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T34 GM137792/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000511/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA230453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK060596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA043703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 NS116842/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA259386/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM127089/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060596/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM128981/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM148662/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

