The metabolic significance of peripheral tissue clocks
- PMID: 40140664
- PMCID: PMC11947457
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-07932-0
The metabolic significance of peripheral tissue clocks
Abstract
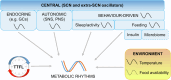
The circadian clock is a transcriptional-translational feedback loop which oscillates in virtually all nucleated cells of the body. In the decades since its discovery, it has become evident that the molecular clockwork is inextricably linked to energy metabolism. Given the frequency with which metabolic dysfunction and clock disruption co-occur, understanding why and how clock and metabolic processes are reciprocally coupled will have important implications for supporting human health and wellbeing. Here, we discuss the relevance of molecular clock function in metabolic tissues and explore its role not only as a driver of day-night variation in gene expression, but as a key mechanism for maintaining metabolic homeostasis in the face of fluctuating energy supply and demand.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kim, H. J. et al. Association between misalignment of circadian rhythm and obesity in Korean men: sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chronobiol. Int.37, 272–280 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Megdal, S. P., Kroenke, C. H., Laden, F., Pukkala, E. & Schernhammer, E. S. Night work and breast cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer41, 2023–2032 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

