Immunomodulatory gene networks predict treatment response and survival to de-escalated, anthracycline-free neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer in the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial
- PMID: 40140821
- PMCID: PMC11938552
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02275-0
Immunomodulatory gene networks predict treatment response and survival to de-escalated, anthracycline-free neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer in the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial
Abstract
Background: Anthracycline-containing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) is the standard treatment for early triple-negative breast cancer (eTNBC); however, it is associated with substantial toxicity. We performed whole transcriptome profiling of baseline tumor biopsies to identify gene networks predictive and prognostic for pathological complete response (pCR) and survival after de-escalated, anthracycline-free NACT in the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial (NCT01815242).
Methods: eTNBC patients (cT1c-cT4c, cN +) were randomized to 12 weeks of nab-paclitaxel + gemcitabine (n = 182) or nab-paclitaxel + carboplatin (n = 154). The primary endpoint was pCR (ypT0/is, ypN0), and the secondary endpoints included survival and translational research. AmpliSeq RNA sequencing, allowing simultaneous analysis of the expression of > 20,000 genes, was performed in 135 patients. Differentially expressed genes were evaluated in training (n = 67) and validation (n = 68) sets, and a polygenic score (PS) for prediction of pCR (PS:pCR) and a PS for prediction of invasive disease-free survival (PS:iDFS) were found.
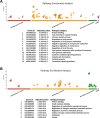
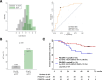
Results: 49/135 (36.3%) patients had pCR; 30 iDFS events occurred during 60-month median follow-up. Immune recruitment and viral defense gene networks were strongly associated with pCR, while metabolic pathways were associated with survival. PS:pCR and PS:iDFS predominantly included immune-related genes. Diagnostic accuracy (ROC AUC) in the validation cohort was 83% for PS:pCR and 64% for PS:iDFS. At optimized cut-off, PS:pCR identified a group with a 67.7% pCR rate (vs. 10.8%; p < .0001), and PS:iDFS detected a group with 79.5% (95%CI 64.1%, 88.8%) 5-year iDFS rate (vs. 55.0%, 95%CI 29.8%, 74.5%; p = .04).
Conclusion: Polygenic scores incorporating immunoregulatory genes can predict pCR and survival and represent an opportunity to select patients for de-escalated, anthracycline-free NACT. This transcriptome network analysis also identifies potential new targets for personalized medicine approaches in patients without response to NACT.
Trial registration: NCT01815242.
Keywords: Biomedical; Gene expression profiling; Gene regulatory networks; Neoadjuvant therapy; Prognosis; Translational research; Triple negative breast neoplasms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Site-specific ethics at the University of Queensland for all translational biomarker work was covered by ethics approval 2015–12-817-PRE-6. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: OG reports honoraria from Genomic Health/Exact Sciences, Roche, Celgene, Pfizer, Novartis, NanoString Technologies, AstraZeneca; consulting or advisory role for Celgene, Genomic Health/Exact Sciences, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Seagen, Pierre Fabre, Gilead, Molecular health; travel support from Roche; all outside of the submitted work; and co-director position at West German Study Group. UN reports honoraria from Agendia, Amgen, Celgene, Genomic Health, NanoString Technologies, Novartis Pharma, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, Roche/Genentech, Teva; consulting or advisory role for Genomic Health, Roche, Seagen; research funding from Agendia (Inst), Amgen (Inst), Celgene (Inst), Genomic Health (Inst), NanoString Technologies (Inst), Roche (Inst), Sanofi (Inst); expert testimony for Genomic Health; travel support from Genomic Health, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, Roche; all outside of the submitted work; and co-director position at West German Study Group. SK reports consulting or advisory role for Amgen, AstraZeneca, Celgene, Daiichi-Sankyo, Genomic Health/Exact Sciences, Lilly, Novartis, Seagen, Pfizer, pfm Medical, Roche, Somatex, Gilead, Roche, MSD Oncology, Sonoscape, Agendia; travel support from Roche, Daiichi Sankyo; research support from Roche, Novartis; fees for non-CME services from Somatex, Roche, Novartis, Lilly; ownership interests for West German Study Group; all outside of the submitted work; and co-director position at West German Study Group. HF reports honoraria from Roche, iOMEDICO; travel support from Celgene, Amgen; all outside of the submitted work. MB reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Exact Sciences, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, MSD; consulting or advisory role for AstraZeneca, Exact Sciences, Novartis, Puma, Roche, Gilead, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Pfizer, Sirius Medical; and travel support from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Medac, Novartis, Roche; all outside of the submitted work. CU reports honoraria from Medi-Semina GmbH, FomF GmbH, RG GmbH für Information, Organisation, Friesland Kliniken—St. Johannes Hospital; consulting or advisory role for Lilly GmbH, Pharma Mar GmbH; research funding from AstraZeneca GmbH, Novartis Pharma GmbH, GBG Forschungs GmbH, Heraclin GmbH, Pierre Fabre Pharma GmbH, Roche AG, Pfizer Pharma GmbH, Universitätsklinikum Ulm, Westdeutsche Studiengruppe GmbH, Alcedis GmbH, AGO Research GmbH, IOMEDICO AG, MMF GmbH; travel support from KelCon Congress & Conferences; speakers' bureau at Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, PharmaMar, AstraZeneca; all outside of the submitted work. BA reports honoraria from Pfizer, Roche Pharma, Merck Sharp & Dohme, onkowissen.de, Novartis Pharma, AstraZeneca, PharmaMar, Lilly, promedicis; all outside of the submitted work. RW reports consulting fees or advisory role, travel support, and speakers' bureau at Agendia, Amgen, Aristo, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Carl Zeiss, Celgene, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Exact Sciences, Genomic Health, Gilead, Glaxo Smith Kline, Hexal, Lilly, Medstrom Medical, MSD, Mundipharma, Mylan, Nanostring, Novartis, Odonate, Paxman, Palleos, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, PumaBiotechnolgogy, Riemser, Roche, Sandoz/Hexal, Sanofi Genzyme, Seattle Genetics /Seagen, Tesaro Bio, Teva, Veracyte, Viatris; and other financial or non-financial interests from FomF (Forum for medical education in Germany), Aurikamed, Clinsol, Pomme Med; all outside of the submitted work. HHK reports honoraria and consulting or advisory role for Lilly, Roche Pharma, Exact Sciences, Astra Zeneca; all outside of the submitted work. MG reports consulting or advisory role for AstraZeneca; travel support from Daiichi Sankyo, AstraZeneca; all outside of the submitted work. NH reports consulting or advisory role for Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz, Seagen; minority ownership interests for West German Study Group; honoraria for lectures from AstraZeneca; Daiichi-Sankyo, Gilead, Novartis; Pfizer; Pierre Fabre; Roche; research funding from Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech (all to institution); and co-director position at West German Study Group. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cortazar P, et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;384(9938):164–72. - PubMed
-
- Schmid P, et al. Overall Survival with Pembrolizumab in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(21):1981–91. - PubMed
-
- Gluz O, et al. Efficacy of deescalated chemotherapy according to PAM50 subtypes, immune and proliferation genes in triple-negative early breast cancer: Primary translational analysis of the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial. Int J Cancer. 2020;146(1):262–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

