Pangenome graph mitigates heterozygosity overestimation from mapping bias: a case study in Chinese indigenous pigs
- PMID: 40140905
- PMCID: PMC11948684
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-025-02194-y
Pangenome graph mitigates heterozygosity overestimation from mapping bias: a case study in Chinese indigenous pigs
Abstract
Background: Breeds genetically distant from the reference genome often show considerable differences in DNA fragments, making it difficult to achieve accurate mappings. The genetic differences between pig reference genome (Sscrofa11.1) and Chinese indigenous pigs may lead to mapping bias and affect subsequent analyses.
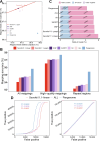
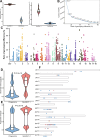
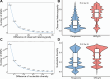
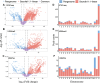
Results: Our analysis revealed that pangenome exhibited superior mapping accuracy to the Sscrofa11.1, reducing false-positive mappings by 1.4% and erroneous mappings by 0.8%. Furthermore, the pangenome yielded more accurate genotypes of SNP (F1: 0.9660 vs. 0.9607) and INDEL (F1: 0.9226 vs. 0.9222) compared to Sscrofa11.1. In real sequencing data, the inconsistent SNPs called from the pangenome exhibited lower genome heterozygosity compared to those identified by the Sscrofa11.1, including observed heterozygosity and nucleotide diversity. The same reduction of heterozygosity overestimation was also found in the chicken pangenome.
Conclusions: This study quantifies the mapping bias of Sscrofa11.1 in Chinese indigenous pigs, demonstrating that mapping bias can lead to an overestimation of heterozygosity in Chinese indigenous pig breeds. The adoption of a pig pangenome mitigates this bias and provides a more accurate representation of genetic diversity in these populations.
Keywords: Genome graph; Mapping bias; Pangenome; Pig; Variant calling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

