Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 40140911
- PMCID: PMC11948873
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-025-01679-1
Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
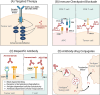
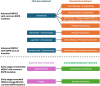
The development of targeted therapy with small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors and immunotherapy with immune checkpoints inhibitors has ushered in the era of precision medicine in treating lung cancer, which remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Both targeted therapy and immunotherapy have significantly improved the survival of patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Additionally, recent groundbreaking studies have demonstrated their efficacy in both the perioperative setting and following concurrent chemoradiotherapy in early-stage NSCLC. Despite significant advancements in first-line treatment options, disease progression remains inevitable for most patients with advanced NSCLC, necessitating the exploration and optimization of subsequent therapeutic strategies. Emerging novel agents are expanding treatment options in the first-line setting and beyond. Recently, emerging bispecific antibodies have shown enhanced efficacy. For instance, amivantamab has been approved as a treatment for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant NSCLC, including those with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Additionally, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), including HER2-targeting trastuzumab deruxtecan, TROP2-targeting ADCs, HER3-targeting patritumab deruxtecan, and MET-targeting telisotuzumab vedotin, have demonstrated promising outcomes in several clinical trials. This review summarizes the recent advancements and challenges associated with the evolving NSCLC therapeutic landscape.
Keywords: Antibody–drug conjugates; Biomarkers; Bispecific antibodies; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; NSCLC; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Targeted therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12–49. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non–small-cell lung cancer to Gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(21):2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu Y-L, Thongprasert S, Yang C-H, Chu D-T, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–57. - PubMed
-
- Jaiyesimi IA, Leighl NB, Ismaila N, Alluri K, Florez N, Gadgeel S, et al. Therapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer with driver alterations: ASCO living guideline, Version 2023.3. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(11):e1–22. - PubMed
-
- Frost N, Reck M. Non-small cell lung cancer metastatic without oncogenic alterations. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2024;44(3):e432524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

