Diagnostic performance of plasma p-tau217 in a memory clinic cohort using the Lumipulse automated platform
- PMID: 40140924
- PMCID: PMC11948696
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-025-01719-5
Diagnostic performance of plasma p-tau217 in a memory clinic cohort using the Lumipulse automated platform
Abstract
Background: Plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease (AD) are a promising tool for accessible and accurate biological diagnostics. However, data in clinical practice are needed to better understand their diagnostic and prognostic ability in memory unit patients.
Methods: We analyzed plasma phosphorylated tau at threonine 217 (p-tau217) and neuroflament light chain (NfL) levels and AD cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers in a group of 493 subjects using the Lumipulse G600II platform. The sample includes 340 patients from our memory unit (142 dementia, 186 mild cognitive impairment, and 12 with subjective complaints) and 153 cognitively unimpaired volunteers. We have correlated plasma and CSF biomarkers; we have analyzed plasma biomarker levels as a function of clinical diagnosis, cognitive status and amyloid status. We have also studied the ability of p-tau217 to discriminate between amyloid-positive and -negative subjects according to CSF using receiver operating characteristic curves.
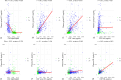
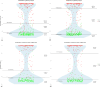
Results: Plasma p-tau217 correlated significantly with CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 (Rho = -0.75; p-value < 0.001), p-tau181 (r = 0.66; p-value < 0.001), and t-tau (r = 0.59; p-value < 0.001). Plasma NfL correlated with CSF NfL (r = 0.48; p-value < 0.001). By clinical diagnosis, plasma p-tau217 levels showed to be higher in AD patients than in healthy controls (difference = 0.63 pg/ml; p-value < 0.001), FTD (difference = 0.60 pg/ml; p-value < 0.001), and nondegenerative dementias (difference = 0.61 pg/ml; p-value < 0.001). Plasma p-tau217 showed an area under the curve of 0.95 to discriminate between A + and A- subjects (95%CI 0.93-0.97).
Conclusion: Plasma p-tau217 shows excellent results for detecting amyloid pathology at brain level in a clinical setting with an AUC of 0.95. It is a highly specific marker of AD and increases progressively along the disease continuum. Using plasma p-tau217 as an initial diagnostic tool with cut-offs at sensitivities and specificities of 95 or 97.5% could save between 57.4-84.8% of LP/PETs with diagnostic accuracies of 95-97%. Plasma NfL increases progressively at different cognitive stages.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Biomarkers; Cross-sectional; Early diagnosis; Healthy controls; Plasma p-tau217.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This research has been conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and has been approved by the ethics committee of the Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla. Title: Valdecilla Cohort for the study of memory and brain aging. Internal code: 2018.111. All subjects have given their signed consent to participate. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2023;388(1):9–21. 10.1056/NEJMoa2212948. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. Drugs@ FDA: FDA... - Google Académico. https://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?journal=Drugs@FDA:+FDA-Approve.... Accessed 28 Aug 2024.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

