The Spectrum of Minimal Change Disease/Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: From Pathogenesis to Proteomic Biomarker Research
- PMID: 40141093
- PMCID: PMC11941885
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062450
The Spectrum of Minimal Change Disease/Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: From Pathogenesis to Proteomic Biomarker Research
Abstract
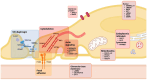
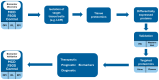
Podocyte injury plays a central role in both focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and minimal change disease (MCD). Pathogenic mechanisms are diverse and incompletely understood, partially overlap between FSGS and MCD, and are not reflected by kidney biopsy. In order to optimize the current variable response to treatment, personalized management should rely on pathogenesis. One promising approach involves identifying biomarkers associated with specific pathogenic pathways. With the advancement of technology, proteomic studies could be a valuable tool to improve knowledge in this area and define valid biomarkers, as they have in other areas of glomerular disease. This work attempts to cover and discuss the main mechanisms of podocyte injury, followed by a review of the recent literature on proteomic biomarker studies in podocytopathies. Most of these studies have been conducted on biofluids, while tissue proteomic studies applied to podocytopathies remain limited. While we recognize the importance of non-invasive biofluid biomarkers, we propose a sequential approach for their development: tissue proteomics could first identify proteins with increased expression that may reflect underlying disease mechanisms; subsequently, the validation of these proteins in urine or plasma could pave the way to a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker-based approach.
Keywords: biomarkers; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; minimal change disease; podocytopathies; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ishizuka K., Miura K., Hashimoto T., Kaneko N., Harita Y., Yabuuchi T., Hisano M., Fujinaga S., Omori T., Yamaguchi Y., et al. Degree of Foot Process Effacement in Patients with Genetic Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis: A Single-Center Analysis and Review of the Literature. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:12008. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91520-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

