β-hydroxy- β-methylbutyrate Attenuates Age-Dependent Loss of Flight Ability and Extends Lifespan in Drosophila
- PMID: 40141306
- PMCID: PMC11941854
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062664
β-hydroxy- β-methylbutyrate Attenuates Age-Dependent Loss of Flight Ability and Extends Lifespan in Drosophila
Abstract
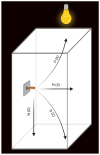
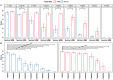
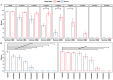
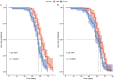
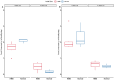
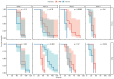
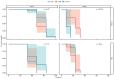
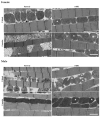
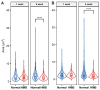
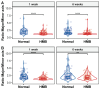
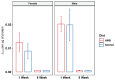
β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) has been shown to enhance muscle function and strength in older humans and rodents after periods of consumption extending for several weeks. We investigated the feasibility of utilizing Drosophila as a model organism to study the biological effects of HMB on aging muscle when consumed throughout adult life. Using flight ability as an index of flight muscle function, we found that HMB attenuates the age-dependent decline in flight ability. Male and female flies fed a diet supplemented with 10 mg/mL HMB had significantly higher flight scores from median age until the onset of flight senescence than control flies fed a standard diet. HMB supplementation also resulted in improved flight scores in males before median age and delayed the onset of flight senescence in females. Notably, the consumption of HMB throughout adult life increased the rate of survival and extended lifespan. The effect on lifespan did not result from changes in food consumption or body weight. Old flies on the HMB-supplemented diet retained a higher proportion of flight muscle mitochondria whose morphology resembled that of young flies than the control diet group. Together, these results suggest that HMB attenuates the age-dependent decline in flight ability and prolongs lifespan by enhancing muscle health.
Keywords: Drosophila; HMB; aging; flight muscle; lifespan; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate (HMB) on age-related functional deficits in mice.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Jan;87(Pt A):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.11.010. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 27887984
-
Dietary HMB and β-alanine co-supplementation does not improve in situ muscle function in sedentary, aged male rats.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015 Dec;40(12):1294-301. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2015-0391. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2015. PMID: 26579948
-
Effects of Running Wheel Activity and Dietary HMB and β-alanine Co-Supplementation on Muscle Quality in Aged Male Rats.J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(5):554-561. doi: 10.1007/s12603-016-0810-2. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017. PMID: 28448086
-
International society of sports nutrition position stand: β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB).J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2434734. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2024.2434734. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39699070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate supplementation and skeletal muscle in healthy and muscle-wasting conditions.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017 Aug;8(4):529-541. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12208. Epub 2017 May 10. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017. PMID: 28493406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

