Enhancing HCV NS3 Inhibitor Classification with Optimized Molecular Fingerprints Using Random Forest
- PMID: 40141322
- PMCID: PMC11943357
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062680
Enhancing HCV NS3 Inhibitor Classification with Optimized Molecular Fingerprints Using Random Forest
Abstract
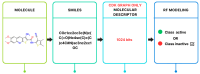
The classification of Hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3 inhibitors is essential for identifying potential antiviral agents through computational methods. This study aims to develop an optimized machine learning (ML) model using random forest (RF) and molecular fingerprints to accurately classify HCV NS3 inhibitors. A dataset of 965 molecules was retrieved from the ChEMBL database, and 290 bioactive compounds were selected for model training. Twelve molecular fingerprint descriptors were tested, and the CDK graph-only fingerprint yielded the best performance. In addition to RF, performance comparisons of other classifiers such as instance-based k-nearest neighbor (IBk), logistic regression (LR), AdaBoost, and OneR were conducted using WEKA with various molecular fingerprint descriptors. The optimized RF model achieved an accuracy of 89.6552%, a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.2114, a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.3304, and a Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) of 0.7950 on the test set. These results highlight the effectiveness of optimized molecular fingerprints in enhancing virtual screening (VS) for HCV inhibitors. This approach offers a data-driven method for drug discovery.
Keywords: HCV NS3 inhibitors; QSAR; computational drug design; machine learning; molecular descriptor optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
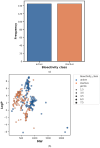
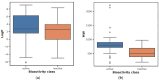

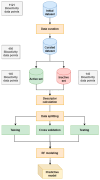
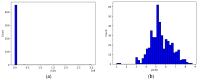
References
-
- World Health Organization Hepatitis C. [(accessed on 20 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c.
-
- Bunally S.B., Luscombe C.N., Young R.J. Using Physicochemical Measurements to Influence Better Compound Design. SLAS Discov. Adv. Life Sci. R&D. 2019;24:791–801. - PubMed
-
- Atasever S. In Silico Drug Discovery: A Machine Learning-Driven Systematic Review. Med. Chem. Res. 2024;33:1465–1490. doi: 10.1007/s00044-024-03260-w. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

