Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Assessment for the Phosphate Transporter 2 Gene Family Within Sweet Potato Under Phosphorus Deficiency Stress
- PMID: 40141323
- PMCID: PMC11942005
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062681
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Assessment for the Phosphate Transporter 2 Gene Family Within Sweet Potato Under Phosphorus Deficiency Stress
Abstract
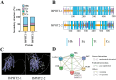
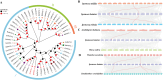
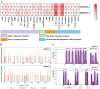
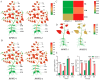
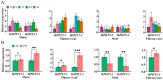
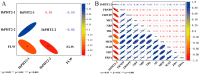
Hainan's unique climate significantly contributes to soil acidification, causing phosphorus fixation into insoluble compounds, leading to phosphorus deficiency and reduced yield in sweet potatoes. The Phosphate Transporter 2 (PHT2) family, a group of trans-membrane phosphate transporters, is crucial for phosphate transport, distribution, and homeostasis regulation. Two PHT2 genes, IbPHT2-1 and IbPHT2-2, were first identified in sweet potato, and a phylogenetic analysis of 46 species showed high conservation of the IbPHT2 gene family throughout plant evolution. Tissue-specific expression patterns of IbPHT2 genes were determined in four sweet potato varieties using transcriptome analysis and RT-qPCR. The results demonstrated that IbPHT2 was predominantly expressed in shoots, mature leaves, stems, and fibrous roots. Under phosphorus deficiency stress, IbPHT2-2 expression was upregulated in shoots, mature leaves, and fibrous roots, with higher expression in mature leaves compared to IbPHT2-1. This observation suggests that, in the context of phosphorus deficiency stress, IbPHT2-2 assumes a more pivotal function in the response mechanism. The expression levels of IbPHT2-2 presented a negative relationship with fresh leaf weight (FLW) as well as fibrous root number per plant (FRNPP) and fibrous root weight per plant (FRWPP) based on correlation analysis. The restrictive function of IbPHT2-2 became impaired by phosphorus deficiency, which resulted in inhibited leaf and root development of sweet potato. The findings of this study provide preliminary evidence that IbPHT2-2 is a key gene involved in the response to phosphorus deficiency stress, influencing phosphorus absorption and distribution in sweet potato. This research contributes to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying phosphorus utilization in sweet potato and may inform future strategies for improving phosphorus use efficiency in this important crop.
Keywords: IbPHT2; phosphorus deficiency stress; sweet potato.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sun R., Wu Z., Chen B., Yang C., Qi D., Lan G., Fraedrich K. Effects of land-use change on eco-environmental quality in Hainan Island, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020;109:105777. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105777. - DOI
-
- Ji C., Liu H., Cha Z., Lin Q., Feng G. Spatial-Temporal Variation of N, P, and K Stoichiometry in Cropland of Hainan Island. Agriculture. 2022;12:39. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12010039. - DOI
-
- Wang D., Huang H., Feng H., Wang H., Han M., Qi Z. Distribution of copper in soil and rice system of Hainan Island, China. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016;59:e16160516
-
- Zhang Q., Chu Y., Xue Y., Ying H., Chen X., Zhao Y., Ma W., Ma L., Zhang J., Yin Y., et al. Outlook of China’s agriculture transforming from smallholder operation to sustainable production. Glob. Food Secur. 2020;26:100444. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100444. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

