Lymphomonocytic Extracellular Vesicles Influence Fibroblast Proliferation and Collagen Production in Systemic Sclerosis
- PMID: 40141341
- PMCID: PMC11942427
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062699
Lymphomonocytic Extracellular Vesicles Influence Fibroblast Proliferation and Collagen Production in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
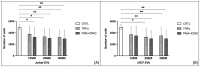
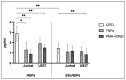
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by fibrosis, immune dysregulation, and vascular abnormalities. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), secreted by immune cells, have been implicated in modulating fibroblast activity and are actively involved in SSc pathogenesis. This study aims to determine whether lymphomonocytic-derived EVs influence fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis in SSc. Fibroblasts from healthy donors (HDFs) and SSc patients (SScHDFs) were exposed to EVs derived from Jurkat and U937 cell lines stimulated under pro-inflammatory conditions using tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate + ionomycin (PMA + IONO). Proliferation was assessed using CCK-8 assays, while collagen production was quantified via ELISA. Our findings demonstrate that EVs derived from PMA + IONO-stimulated Jurkat and U937 cells significantly reduced fibroblast proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Notably, SScHDFs exhibited lower baseline proliferation and a diminished overall response to EV treatment. Collagen production was markedly reduced in both fibroblast types following exposure to PMA + IONO-stimulated EVs, whereas TNFα-stimulated EVs affected only HDFs. These findings suggest that EVs from activated immune cells modulate fibroblast function in SSc, potentially contributing to disease pathogenesis. Further research is warranted to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying these effects and to explore the therapeutic potential of targeting EV-mediated signaling in SSc.
Keywords: Jurkat; U937; extracellular vesicles; fibroblasts; fibrosis; systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Th17 cells favor inflammatory responses while inhibiting type I collagen deposition by dermal fibroblasts: differential effects in healthy and systemic sclerosis fibroblasts.Arthritis Res Ther. 2013 Oct 10;15(5):R151. doi: 10.1186/ar4334. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013. PMID: 24289089 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of scleroderma. Collagen.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996 Nov;22(4):647-74. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70294-5. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996. PMID: 8923589 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Are More Potent Than Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Exert an Anti-Fibrotic Effect in an In Vitro Model of Systemic Sclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6837. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136837. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34202139 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in scleroderma: maintenance of scleroderma fibroblast phenotype by the constitutive up-regulation of reactive oxygen species generation through the NADPH oxidase complex pathway.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Nov;44(11):2653-64. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2653::aid-art445>3.0.co;2-1. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11710721
-
Regulation of connective tissue synthesis in systemic sclerosis.Int Rev Immunol. 1995;12(2-4):187-99. doi: 10.3109/08830189509056712. Int Rev Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7650421 Review.
References
-
- Mostmans Y., Cutolo M., Giddelo C., Decuman S., Melsens K., Declercq H., Vandecasteele E., De Keyser F., Distler O., Gutermuth J., et al. The Role of Endothelial Cells in the Vasculopathy of Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017;16:774–786. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.05.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yoshimatsu Y., Wakabayashi I., Kimuro S., Takahashi N., Takahashi K., Kobayashi M., Maishi N., Podyma-Inoue K.A., Hida K., Miyazono K., et al. TNF-α Enhances TGF-β-Induced Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via TGF-β Signal Augmentation. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:2385–2399. doi: 10.1111/cas.14455. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Distler J.H.W., Jungel A., Huber L.C., Seemayer C.A., Reich C.F., Gay R.E., Michel B.A., Fontana A., Gay S., Pisetsky D.S., et al. The Induction of Matrix Metalloproteinase and Cytokine Expression in Synovial Fibroblasts Stimulated with Immune Cell Microparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:2892–2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409781102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

