Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng
- PMID: 40141343
- PMCID: PMC11942579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062701
Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng
Abstract
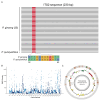
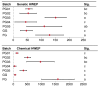
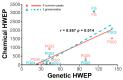
Quality control remains a challenge in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). This study introduced a novel genetic-based quality control method for TCM. Genetic variations in ginseng were evaluated across whole-genome, chloroplast genome, and ITS2 DNA barcode dimensions. Significant genetic variations were found in whole-genome comparison, leading to the use of inter-simple sequence repeat markers to assess the genetic diversity of ginseng decoction pieces (PG), garden ginseng (GG), and ginseng under forest (FG). Fingerprints of ginseng samples revealed instability within some batches. These evaluations were transformed into information entropy to calculate the size of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium population (HWEP). FG had significantly higher genetic and chemical minimum HWEP than GG (p < 0.05). Notably, a significant positive correlation was observed between the minimum HWEP for genetics and for chemistry (r = 0.857, p = 0.014). Genetic polymorphism analysis of ginseng has the potential to evaluate chemical quality consistency, offering a new method to ensure quality consistency in TCM.
Keywords: HWEP; Panax ginseng; genetic polymorphism; quality consistency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hu Y., Zhang Q.Y., Xin H.L., Qin L.P., Lu B.R., Rahman K., Zheng H.C. Association between chemical and genetic variation of Vitex rotundifolia populations from different locations in China: Its implication for quality control of medicinal plants. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007;21:967–975. doi: 10.1002/bmc.841. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

