Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I
- PMID: 40141345
- PMCID: PMC11943261
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062704
Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I
Abstract
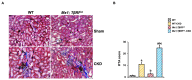
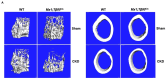
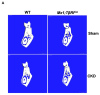
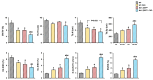
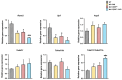
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β), a master regulator of renal fibrosis, is the hallmark of chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression, and CKD worsens bone remodeling. However, the effects of the dysregulation of TGF-β signaling on bone remodeling during CKD have not been investigated. Here, we determined the effects of TGF-β receptor I (TβRI) overexpression under the control of Mx1-Cre on bone remodeling in CKD mice (Mx1;TβRICA-CKD mice). Our results demonstrated that kidney fibrosis and serum urea nitrogen levels were elevated in Mx1;TβRICA-CKD mice compared to WT-CKD, indicating that TβRI overexpression exacerbated renal injury during CKD. Serum calcium was decreased, while PTH was enhanced, in Mx1;TβRICA-CKD mice. Mx1;TβRICA-CKD mice displayed severe osteopenia as assessed by uCT in both femurs and mandibles. An histomorphometric analysis showed that tibial cancellous bone volume was decreased in Mx1;TβRICA-CKD. Likewise, mRNA expression levels of an osteoclastogenesis marker, Tnfsf11/Tnfrsf11b, was increased, and osteoblast marker genes Runx2 and Sp7 were decreased in Mx1;TβRICA-CKD mice. Mx1;TβRICA-CKD mice displayed increased inflammatory cytokines levels. Together, our results indicated that in the setting of CKD, TβRI overexpression induced both CKD progression and the dysregulation of bone remodeling, leading to severe bone loss. As such, these data provide an avenue for the future development of therapeutics for CKD-induced osteoporosis.
Keywords: TGFβ; bone; chronic kidney disease; osteoblast; osteoclast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
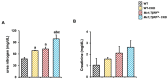
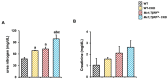
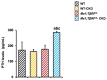



References
-
- Shull M.M., Ormsby I., Kier A.B., Pawlowski S., Diebold R.J., Yin M., Allen R., Sidman C., Proetzel G., Calvin D., et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature. 1992;359:693–699. doi: 10.1038/359693a0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karsdal M.A., Larsen L., Engsig M.T., Lou H., Ferreras M., Lochter A., Delaissé J.-M., Foged N.T. Matrix Metalloproteinase-dependent Activation of Latent Transforming Growth Factor-β Controls the Conversion of Osteoblasts into Osteocytes by Blocking Osteoblast Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:44061–44067. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207205200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yasui T., Kadono Y., Nakamura M., Oshima Y., Matsumoto T., Masuda H., Hirose J., Omata Y., Yasuda H., Imamura T., et al. Regulation of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by TGF-β through molecular interaction between Smad3 and Traf6. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011;26:1447–1456. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.357. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

