AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 40141386
- PMCID: PMC11943011
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26062744
AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis
Abstract
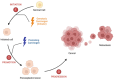
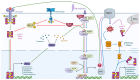
Human chemical carcinogenesis is a multistage process where chemicals or their metabolites cause irreversible changes in normal cell physiology, eventually leading to uncontrolled proliferation, transforming a normal cell into a cancerous one. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a cytoplasmic transcription factor that regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, inflammation, and immune responses. Its aberrant activation triggers tumor progression by promoting the expression of oncogenic genes; thus, STAT3 is classified as an oncoprotein. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that responds to a wide variety of chemicals, including carcinogens like dioxins, inducing genes associated with detoxification, proliferation, and immune regulation. Recent reports show that AhR plays a critical role in cancer development and maintenance. AhR may interact with signaling pathways, like the STAT3 pathway, which mediates the carcinogenic effects of several pollutants. Various chemical agents, such as industrial waste and hydrocarbon compounds, can alter the expression or signaling activity of AhR and STAT3 pathways, leading to different types of cancers. Understanding the complex STAT3-AhR network in the regulation of chemical carcinogenesis could open new avenues for cancer prevention or treatment, particularly in personalized medicine, aiming to improve life expectancy and achieving a complete cure.
Keywords: AhR; STAT3; chemical carcinogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kabirai A., Chahar A., Chahar N., Gupta J. Chemical carcinogenesis: A brief review on mechanism & metabolism. J. Oral Med. Oral Surg. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020;6:120–124. doi: 10.18231/j.jooo.2020.027. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

